Abstract
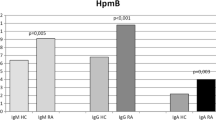
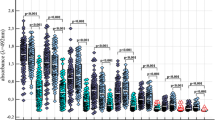
In a survey of 89 RA patients, carried out under code,Proteus mirabilis was isolated from the urine of 63% (47/75) of female (P<0.001) and 50% (7/14) of male patients (P<0.001) compared to a frequency of isolation in healthy women of 32% (38/119) and 11% (13/115) in healthy men. There was no significant difference in isolation rates between 37 non-RA patients and healthy controls. Sera from 20 patients with RA and 20 healthy controls were tested againstP. mirabilis andEscherichia coli by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Antibodies againstP. mirabilis but not toE. coli were significantly higher in the RA patients than in healthy controls (P<0.001). Furthermore, a positive correlation was found between high anti-Proteus antibody levels in serum samples and the number of Proteus colony-forming units obtained from urine specimens of the 20 RA patients (r=+0.714,P<0.001). These results support the suggestion of an aetiopathogenic role forP. mirabilis in RA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ebringer A, Ptaszynska T, Corbett M, Wilson C, Macaffee Y, Avakian H, Baron P, James DCO (1985) Antibodies toProteus in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet II:305–307
Deighton CM, Gray JW, Bint AJ, Walker DJ (1992) Anti-Proteus antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis same-sexed sibships. Br J Rheumatol 31:241–245
Rogers P, Hassan J, Breshnihan B, Feighery C, Whelan A (1988) Antibodies toProteus in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol 27 [Suppl 11]:90–94
Watanabe Y, Tokunaga K, Matsuki K, Takeuchi F, Matsuta K, Maeda A, Omoto K, Juji T (1989) Putative amino acid sequene of HLA DRβ chain contributing to rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility. J Exp Med 169:2263–2268
Wilson C, Ebringer A, Ahmadi K, Wrigglesworth J, Tiwana H, Fielder M, Binder A, Ettelaie C, Cunningham P, Joannou C, Bansal S (1995) Shared amino acid sequences between major histocompatibility complex class II glycoproteins, type XI collagen andProteus mirabilis in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 54:216–220
Khalafpour S, Ebringer A, Abuljadayel I, Corbett M (1988) Antibodies toKlebsiella andProteus microorganisms in ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis patients measured by ELISA. Br J Rheumatol 27 [Suppl II]:86–89
McDonagh J, Gray J, Sykes H, Walker DJ, Bint AS, Deighton CM (1994) Anti-Proteus antibodies andProteus organisms in rheumatoid arthritis: a clinical study. Br J Rheumatol 33:32–35
Fairley KF, Grounds AD, Carson NE, Laird EC, Gutch RC, McCallum PHG, Leighton P, Sleeman RL, O'Keefe CM (1971) Site of infection in acute urinary tract infection in general practice. Lancet II:615–618
Tishler M, Caspi D, Aimog Y, Segal R, Yaron M (1992) Increased incidence of urinary tract infection in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and Sjögren's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 51:604–606
Fielder M, Tiwana H, Youinou P, Legoff P, Deonarain R, Wilson C, Ebringer A (1995) The specificity of the anti-Proteus antibody response in tissue-type rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients from Brest. Rheumatol Int 15:79–82
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilson, C., Thakore, A., Isenberg, D. et al. Correlation between anti-Proteus antibodies and isolation rates ofP. mirabilis in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 16, 187–189 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01330294
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01330294