Abstract
Objective
This study investigated differences in subcortical brain volumes of SLE patients with cognitive deficits (SLE-CD) and SLE patients with normal cognitive performance (SLE-CN), regardless of the presence of other neuropsychiatric symptoms.
Method
We studied 40 patients divided into two-matched groups (SLE-CD n = 20; SLE-CN n = 20), with age ranging from 21 to 63 years old (100 % female) and 14.73 ± 10.18 years of diagnosis. Magnetic resonance imaging exams were performed on a 1.5 T scanner. A neuropsychological flexible battery was applied individually, including reasoning/problem-solving, praxis, episodic and working memory, processing speed, language/fluency, executive functions (inhibition and flexibility), and sustained attention. Z score ≤ − 2.0 in any dimension was considered as a cut-off for being considered to possess cognitive deficits. One-way analyses of covariance (ANCOVA) were performed to compare the brain structure volumes between groups. The analyses were controlled for the effects of lupus-related neuropsychiatric disorders.
Results
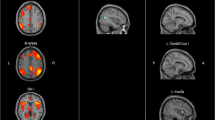
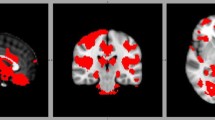
SLE patients with cognitive deficits had significantly smaller volumes in the left hippocampus, amygdala, and the right hippocampus than SLE patients without cognitive deficits.
Conclusion
SLE patients with cognitive deficits appeared to have reduced temporal lobe structures when compared with SLE without cognitive deficits. These results corroborate a systems vulnerability model that investigated temporal lobe vulnerability during normal aging and in other neurological disorders.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
ACR AC of RAHC. The American College of Rheumatology nomenclature and case definitions for neuropsychiatric lupus syndromes. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42(4):599–608.
Carlomagno S, Migliaresi S, Ambrosone L, Sannino M, Sanges G, Di Iorio G. Cognitive impairment in systemic lupus erythematosus: a follow-up study. J Neurol. 2000;247:273–9.
Nowicka-Sauer K, Czuszyńska Z, Smoleńska Ż, Siebert J. Neuropsychological assessment in systemic lupus erythematosus patients: clinical usefulness of first-choice diagnostic tests in detecting cognitive impairment and preliminary diagnosis of neuropsychiatric lupus. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2011;29:299–306.
Monastero R, Bettini P, Del E, Cottini E, Tincani A, Balestrieri G, Cattaneo R, Camarda R, Vignolo LA, Padovani A. Prevalence and pattern of cognitive impairment in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with and without overt neuropsychiatric manifestations. J Neurol Sci. 2001;184:33–9.
Cagnoli P, Sundgren P, Kairys A, Graft C, Clauw D, Gebarski S, McCune WJ, Schmidt-Wilcke T. Changes in regional brain morphology in neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 2012;29:959–67.
Muscal E, Brey RL. Neurologic manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus in children and adults. Neurol Clin. 2010;28(1):61–73 (Elsevier Ltd).
Kozora E, Arciniegas DB, Filley CM, West SG, Brown M, Miller D, Grimm A, Devore MD, Wingrove C, Zhang L. Cognitive and neurologic status in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus without major neuropsychiatric syndromes. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59(11):1639–46.
Danchenko N, Satia J, Anthony M. Epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus: a comparison of worldwide disease burden. Lupus. 2006;15(5):308–18.
Bruns A, Meyer O. Neuropsychiatric manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Joint Bone Spine. 2006;73(6):639–45.
Hanly JG. ACR classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus: limitations and revisions to neuropsychiatric variables. Lupus. 2004;13(11):861–4.
Unterman A, Nolte JES, Boaz M, Abady M, Shoenfeld Y, Zandman-Goddard G. Neuropsychiatric syndromes in systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2011;41(1):1–11
Vogel A, Bhattacharya S, Larsen JL, Jacobsen S. Do subjective cognitive complaints correlate with cognitive impairment in systemic lupus erythematosus? A Danish outpatient study. Lupus. 2011;20(1):35–43.
Ainiala H, Hietaharju A, Loukkola J, Peltola J, Korpela M, Metsänoja R, Auvinen A. Validity of the New American College of Rheumatology Criteria for Neuropsychiatric Lupus Syndromes: a population-based evaluation. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Oct;45(5):419-23.
Appenzeller S, Rondina JM, Li LM, Costallat LTL, Cendes F. Cerebral and corpus callosum atrophy in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(9):2783–9.
Kozora E, Ellison MC, West S. Reliability and validity of the proposed American College of Rheumatology neuropsychological battery for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;51(5):810–8.
Appenzeller S, Vasconcelos Faria A, Li LM, Costallat LTL, Cendes F. Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging analyses and clinical significance of hyperintense white matter lesions in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Ann Neurol. 2008;64(6):635–43.
Gauthier L, Dehaut F, Joanette Y. The Bells Test. Int J Clin Neuropsychol. 1989;6:48–54.
Fonseca RP, Oliveira C, Gindri G, Zimmermann N, Reppold C. Teste Hayling: um instrumento de avaliação de componentes das funções executivas. In: Hutz C, editor. Avaliação psicológica e neuropsicológica de crianças e adolescentes. São Paulo: Casa do Psicólogo; 2010. pp. 337–64.
Burgess PW, Shallice T. The Hayling and Brixton Tests. Thurston: Thames Valley Test Company; 1997.
AIT AITB. Army Individual Test Battery. Washington: War Department, Adjutant General’s Office; 1944.
Fonseca RP, Parente MA de MP, Côté H, Ska B, Joanette Y. Bateria Montréal de Avaliação da Comunicação—Bateria MAC. São Paulo: Pró-Fono; 2008.
Fonseca RP, Joanette Y, Côté H, Ska B, Giroux F, Fachel JM, Damasceno Ferreira G, Parente MA. Brazilian version of the Protocole Montréal d’Evaluation de la Communication (Protocole MEC): normative and reliability data. Span J Psychol. 2008;11:678–88.
do Nascimento E. Adaptação, validação e normatização do WAIS-III para uma amostra brasileira. In: Wechsler D, editor. WAIS III: manual para administração e avaliação. São Paulo: Casa do Psicólogo; 2004.
de Figueiredo VLM, do Nascimento E. Desempenhos nas duas tarefas do subteste Dígitos do WISC-III e do WAIS-III. Psicol Teor e Pesqui. 2007;23(3):313–8.
Nascimento E, de Figueiredo VLM. WISC-III and WAIS-III: Alterations in the current American original versions of the adaptations for use in Brazil. Psicol Reflexão e Crítica. 2002;15:603–12.
Fonseca RP, de Salles JF, Parente MA de MP. Instrumento de Avaliação Neuropsicológica Breve NEUPSILIN. São Paulo: Vetor; 2009.
Salgado JV, Malloy-Diniz LF, Abrantes SS, Moreira L, Schlottfeldt CG, Guimarães W, Freitas DM, Oliveira J, Fuentes D. Applicability of the Rey Auditory-Verbal Learning Test to an adult sample in Brazil. Rev Bras Psiquiatr. 2011;33(3):234–7.
Nelson HE. A modified card sorting test sensitive to frontal lobe defects. Cortex. 1976;12(4):313–24.
Hatanpaa KJ, Raisanen JM, Herndon E, Burns DK, Foong C, Habib AA, White CL 3rd. Hippocampal subfields in dementia, epilepsy, and ischemic injury: differential vulnerability of hippocampal subfields. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2014;73(2):136–42.
Buckner RL, Krienen FM. The evolution of distributed association networks in the human brain. Trends Cogn Sci. 2013;17(12):648–65.
Fjell AM, Amlien IK, Sneve MH, Grydeland H, Tamnes CK, Chaplin TA, Rosa MG, Walhovd KB. The roots of Alzheimer’s disease: are high-expanding cortical areas preferentially targeted? Cereb Cortex. 2014 Mar 21. [Epub ahead of print]
Jagust W. Vulnerable neural systems and the borderland of brain aging and neurodegeneration. Neuron. 2014;77(2):219–34.
Kerchner GA, Bernstein JD, Fenesy MC, Deutsch GK, Saranathan M, Zeineh MM, Rutt BK. Shared vulnerability of two synaptically-connected medial temporal lobe areas to age and cognitive decline: a seven tesla magnetic resonance imaging study. J Neurosci. 2013;33(42):16666–72.
Toyota T, Akamatsu N, Tanaka A, Shouzaki T, Tsuji S, Saito K, Tanaka Y. Mesial temporal lobe epilepsy as a neuropsychiatric syndrome of systemic lupus erythematosus. Epilepsia. 2013;54(3):e33–6.
Xu J, Cheng Y, Chai P, Lu Z, Li H, Luo C, Li X, Li L, Zhou Q, Chen B, Cao J, Xu X, Shan B, Xu L, Wen J. White-matter volume reduction and the protective effect of immunosuppressive therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with normal appearance by conventional magnetic resonance imaging. J Rheumatol. 2010;37(5):974–86.
Appenzeller S, Carnevalle AD, Li LM, Costallat LTL, Cendes F. Hippocampal atrophy in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65(12):1585–9.
Ren T, Ho RC, Mak A. Dysfunctional cortico-basal ganglia-thalamic circuit and altered hippocampal-amygdala activity on cognitive set-shifting in non-neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(12):4048–59.
Cagnoli PC, Sundgren PC, Kairys A, Graft CC, Clauw DJ, Gebarski S, McCune WJ, Schmidt-Wilcke T. Changes in regional brain morphology in neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 2012;39(5):959–67.
Acknowledgments
We thank Denise Vieira Greca and Bernardo Bizzo for their work on data collection.
Funding
This work was supported by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (Brazil) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (Brazil).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zimmermann, N., Corrêa, D., Kubo, T. et al. Global Cognitive Impairment in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients: A Structural MRI Study. Clin Neuroradiol 27, 23–29 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-015-0397-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-015-0397-8