Abstract
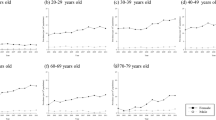
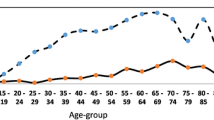
This population-based study aimed to determine the trend of incidence, prevalence, and mortality of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in a 6-year period in Taiwan. Patients with international classification of diseases ninth revision (ICD-9) code 710.0 were retrieved from the Taiwanese National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD), which covered more than 96 % of the entire population, and from the Ministry of Interior between 2003 and 2008 in Taiwan. Patients with SLE registered as catastrophic illness were enrolled for analysis. The incidence rate, prevalence ratio, and mortality rate stratified by sex and age were analyzed. There were a total of 6,675 SLE patients (5,836 females and 839 in males) during the study period. The average annual incidence rate was 4.87 per 100,000 population, and the average female-to-male incidence ratio was 7.15. The ratio increased with age and peaked at the age of 40–49 years, then decreased thereafter. The incidence rate decreased by 4.2 % per year. The highest incidence rate was noted in the 20–29-year-old age group in females and the 70–79-year-old age group in males. The average prevalence and mortality rates were 97.5 and 1.2 per 100,000 population, respectively. Mortality was 3.2 % in patients diagnosed within 1 year and is more prevalent in young patients with average age of 15.6 years. Incidence rate of SLE has been declining in recent years but the prevalence rate has remained steady. The highest mortality rate is among younger patients diagnosed with SLE within 1 year.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pons-Estel GJ, Alarcón GS, Scofield L, Reinlib L, Cooper GS (2010) Understanding the epidemiology and progression of systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthr Rheum 39:257–268
Moradinejad MH, Zamani GR, Kiani AR, Esfahani T (2008) Clinical features of juvenile lupus erythematosus in Iranian children. Acta Rheumatol Port 33:63–67
Fessel WJ (1988) Epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 14:15–23
Fujukawa S, Okuni M (1997) A national study of rheumatic diseases among Japanese children. Acta Paediatr Jpn 39:242–244
Malleson PJ, Fung MY, Rosenberg AM (1996) The incidence of pediatric rheumatic diseases: results from the Canadian pediatric rheumatology association disease registry. J Rheumatol 23:1981–1987
Mok CC, To CH, Ho LY, Yu KL (2008) Incidence and mortality of systemic lupus erythematosus in a Southern Chinese Population, 2000–2006. J Rheumatol 35:1978–1982
Mok CC (2011) Epidemiology and survival of systemic lupus erythematosus in Hong Kong Chinese. Lupus 20:767–771
Uramoto KM, Michet J, Thumboo J, Sunku J, O’Fallon WM, Gabriel SE (1999) Trends in the incidence and mortality of systemic lupus erythematosus, 1950–1992. Arthr Rheum 42:46–50
Somers EC, Thomas SL, Smeeth L, Schoonen WM, Hall AJ (2007) Incidence of systemic lupus erythematosus in the United Kingdom, 1990–1999. Arthr Rheum 57:612–618
Eilertsen GØ, Fismen S, Hanssen TA, Nossent JC (2011) Decreased incidence of lupus nephritis in northern Norway is linked to increased use of antihypertensive and anticoagulant therapy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26:620–627
Osio-Salido E, Manapat-Reyes H (2010) Epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus in Asia. Lupus 19:1365–1373
Kamphuis S, Silverman ED (2010) Prevalence and burden of pediatric-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Rev Rheumatol 6:538–546
Huang JL, Yao TC, See LC (2004) Prevalence of pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus and juvenile chronic arthritis in a Chinese population: a nationwide prospective population-based study in Taiwan. Clin Exp Rheumatol 22:776–780
Chiu YM, Lai CH (2010) Nationwide population-based epidemiologic study of systemic lupus erythematosus in Taiwan. Lupus 19:1250–1255
Cervera R, Khamashta MA, Hughes GRV (2009) The Euro-lupus project: epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus in Europe. Lupus 18:869–874
Kariuki SN, Moore JG, Kirou KA, Crow MK, Utset TO, Niewold TB (2009) Age- and gender-specific modulation of serum osteopontin and interferon-[alpha] by osteopontin genotype in systemic lupus erythematosus. Genes Immun 10:487–494
Kaslow RA (1982) High rate of death caused by systemic lupus erythematosus among U.S. residents of Asian descent. Arthr Rheum 25:414–418
Johnson SR, Urowitz MB, Ibañez D, Gladman DD (2006) Ethnic variation in disease patterns and health outcomes in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 33:1990–1995
Bernatsky S, Boivin JF, Joseph L et al (2006) Mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthr Rheum 54:2550–2557
Chen MJ, Tseng HM, Huang YL et al (2008) Long-term outcome and short-term survival of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus after bacteraemia episodes: 6-yr follow-up. Rheumatology 47:1352–1357
Chang DM, Chang CC, Kuo SY, Chu SJ, Chang ML (1998) The clinical features and prognosis of male lupus in Taiwan. Lupus 7:462–468
Prete PE, Majlessi A, Gilman S, Hamideh F (2001) Systemic lupus erythematosus in men: a retrospective analysis in a Veterans administration healthcare system population. J Clin Rheumatol 73:142–150
Manger K, Manger B, Repp R et al (2002) Definition of risk factors for death, end stage renal disease, and thrombo-embolic events in a monocentric cohort of 338 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 61:1065–1070
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Kuo-Wei Yeh and Chong-Hua Yu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeh, KW., Yu, CH., Chan, PC. et al. Burden of systemic lupus erythematosus in Taiwan: a population-based survey. Rheumatol Int 33, 1805–1811 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-012-2643-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-012-2643-6