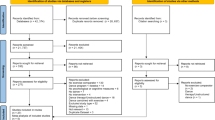
Abstract
Physical activity (PA) is associated with numerous health-related benefits among adults with chronic diseases and the general population. As the benefits are dose-dependent, this review aims to establish the PA levels of adults with spondyloarthritis and to compare these to the general population. Electronic databases (Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, EMBASE, MEDLINE/PubMed, PEDro, AMED, CINAHL) were systematically searched from inception to May 2014 using medical subject headings and keywords. This was supplemented by searching conference abstracts and hand-searching reference lists of included studies. Eligible studies were randomized controlled trials and observational studies of adults with SpA in which free-living PA or energy expenditure levels were measured. Subjects less than 18 years or with juvenile-onset SpA were excluded. Outcomes included objective and self-report measurements. Two reviewers independently screened studies for inclusion and assessed methodological quality using the Cochrane risk of bias tool and the RTI item bank. From the 2,431 records reviewed, nine studies involving 2,972 participants were included. This review focused on qualitative synthesis. Meta-analyses were not undertaken due to differences in study design, measurement tools, and participant characteristics. This heterogeneity, coupled with the risk of bias inherent in the included observational studies, limits the generalizability of findings. Objective measurements suggest PA levels may be lower among adults with spondyloarthritis than in healthy population controls. Self-reported PA and self-reported rates of adherence to PA recommendations varied largely across studies; higher disease activity was associated with lower self-reported PA levels. Physical activity levels may be lower in adults with axial spondyloarthritis, with higher disease activity associated with lower PA levels.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zochling J, Brandt J, Braun J (2005) The current concept of spondyloarthritis with special emphasis on undifferentiated spondyloarthritis. Rheumatology 44(12):1483–1491
Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Landewe R, Listing J, Akkoc N, Brandt J, Braun J, Chou CT, Collantes-Estevez E, Dougados M, Huang F, Gu J, Khan MA, Kirazli Y, Maksymowych WP, Mielants H, Sorensen IJ, Ozgocmen S, Roussou E, Valle-Onate R, Weber U, Wei J, Sieper J (2009) The development of assessment of spondyloarthritis international society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part II): validation and final selection. Ann Rheum Dis 68(6):777–783. doi:10.1136/ard.2009.108233
Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Landewe R, Akkoc N, Brandt J, Chou CT, Dougados M, Huang F, Gu J, Kirazli Y, Van den Bosch F, Olivieri I, Roussou E, Scarpato S, Sorensen IJ, Valle-Onate R, Weber U, Wei J, Sieper J (2011) The assessment of spondyloarthritis international society classification criteria for peripheral spondyloarthritis and for spondyloarthritis in general. Ann Rheum Dis 70(1):25–31. doi:10.1136/ard.2010.133645
Singh JA, Strand V (2009) Spondyloarthritis is associated with poor function and physical health-related quality of life. J Clin Rheumatol Pract Rep Rheumat Musculoskelet Dis 36(5):1012–1020
Heikkila S, Viitanen JV, Kautiainen H, Kauppi M (2002) Functional long-term changes in patients with spondyloarthropathy. Clin Rheumatol 21(2):119–122
Haglund E, Bremander A, Bergman S, Jacobsson LTH, Petersson IF (2013) Work productivity in a population-based cohort of patients with spondyloarthritis. Rheumatology 52(9):1708–1714
Papagoras C, Voulgari PV, Drosos AA (2013) Atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease in the spondyloarthritides, particularly ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 31(4):612–620
Han C, Robinson DW Jr, Hackett MV, Paramore LC, Fraeman KH, Bala MV (2006) Cardiovascular disease and risk factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol 33(11):2167–2172
Braun J, Van Den Berg R, Baraliakos X, Boehm H, Burgos-Vargas R, Collantes-Estevez E, Dagfinrud H, Dijkmans B, Dougados M, Emery P, Geher P, Hammoudeh M, Inman RD, Jongkees M, Khan MA, Kiltz U, Kvien TK, Leirisalo-Repo M, Maksymowych WP, Olivieri I, Pavelka K, Sieper J, Stanislawska-Biernat E, Wendling D, Ozgocmen S, Van Drogen C, Van Royen BJ, Van Der Heijde D (2011) 2010 update of the ASAS/EULAR recommendations for the management of ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 70(6):896–904
Ritchlin CT, Kavanaugh A, Gladman DD, Mease PJ, Helliwell P, Boehncke WH, De Vlam K, Fiorentino D, FitzGerald O, Gottlieb AB, McHugh NJ, Nash P, Qureshi AA, Soriano ER, Taylor WJ (2009) Treatment recommendations for psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 68(9):1387–1394
O’Dwyer T, O’Shea F, Wilson F (2014) Exercise therapy for spondyloarthritis: a systematic review. Rheumatol Int 34(7):887–902
Caspersen CJ, Powell KE, Christenson GM (1985) Physical activity, exercise, and physical fitness: definitions and distinctions for health-related research. Public Health Rep (Washington, DC: 1974) 100(2):126–131
Warburton DE, Nicol CW, Bredin SS (2006) Health benefits of physical activity: the evidence. CMAJ 174(6):801–809. doi:10.1503/cmaj.051351
Donnelly JE, Blair SN, Jakicic JM, Manore MM, Rankin JW, Smith BK (2009) American College of Sports Medicine Position Stand. Appropriate physical activity intervention strategies for weight loss and prevention of weight regain for adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc 41(2):459–471. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181949333
Global recommendations on physical activity for health. World Health Organization (2010)
Nelson ME, Rejeski WJ, Blair SN, Duncan PW, Judge JO, King AC, Macera CA, Castaneda-Sceppa C (2007) Physical activity and public health in older adults: recommendation from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association. Med Sci Sports Exerc 39(8):1435–1445. doi:10.1249/mss.0b013e3180616aa2
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, Moher D, Becker BJ, Sipe TA, Thacker SB (2000) Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 283(15):2008–2012
Higgins JP, Green S (eds) (2011) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. The Cochrane Collaboration. Available from http://www.cochrane-handbook.org. Accessed 7 March 2011
Viswanathan M, Berkman ND, Dryden DM, Hartling L (2013) Assessing risk of bias and confounding in observational studies of interventions or exposures: further development of the RTI Item Bank. Rockville
Van Genderen S, Van Den Borne C, Geusens P, Van Der Linden S, Boonen A, Plasqui G (2014) Physical functioning in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: comparing approaches of experienced ability with self-reported and objectively measured physical activity. J Clin Rheumatol Pract Rep Rheumat Musculoskelet Dis 20(3):133–137
Plasqui G, Boonen A, Geusens P, Kroot EJ, Starmans M, Van Der Linden S (2012) Physical activity and body composition in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 64(1):101–107
Halvorsen S, Vollestad NK, Fongen C, Provan SA, Semb AG, Hagen KB, Dagfinrud H (2012) Physical fitness in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: comparison with population controls. Phys Ther 92(2):298–309. doi:10.2522/ptj.20110137
Fongen C, Halvorsen S, Dagfinrud H (2013) High disease activity is related to low levels of physical activity in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Rheumatol 32(12):1719–1725
Manning VL, Hurley MV, Scott DL, Bearne LM (2012) Are patients meeting the updated physical activity guidelines? Physical activity participation, recommendation, and preferences among inner-city adults with rheumatic diseases. J Clin Rheumatol Pract Rep Rheumat Musculoskelet Dis 18(8):399–404
O’Dwyer T, Rafferty T, O’Shea F, Gissane C, Wilson F (2014) Physical activity guidelines: is the message getting through to adults with rheumatic conditions? Rheumatology 53(10):1812–1817
Niedermann K, Sidelnikov E, Muggli C, Dagfinrud H, Hermann M, Tamborrini G, Ciurea A, Bischoff-Ferrari H (2013) Effect of cardiovascular training on fitness and perceived disease activity in people with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthrit Care Res 65(11):1844–1852
Arends S, Hofman M, Kamsma YPT, der Veer EV, Houtman PM, Kallenberg CGM, Spoorenberg A, Brouwer E (2013) Daily physical activity in ankylosing spondylitis: validity and reliability of the IPAQ and SQUASH and the relation with clinical assessments. Arthritis Res Ther 15(4):R99. doi:10.1186/ar4279
Swinnen TW, Scheers T, Lefevre J, Dankaerts W, Westhovens R, de Vlam K (2014) Physical activity assessment in patients with axial spondyloarthritis compared to healthy controls: a technology-based approach. PLoS ONE 9(2):e85309. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0085309
Haglund E, Bergman S, Petersson IF, Jacobsson LT, Strombeck B, Bremander A (2012) Differences in physical activity patterns in patients with spondylarthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 64(12):1886–1894. doi:10.1002/acr.21780
Brophy S, Cooksey R, Davies H, Dennis MS, Zhou SM, Siebert S (2013) The effect of physical activity and motivation on function in ankylosing spondylitis: a cohort study. Semin Arthritis Rheu 42(6):619–626
Ehrlich-Jones L, Lee J, Semanik P, Cox C, Dunlop D, Chang RW (2011) Relationship between beliefs, motivation, and worries about physical activity and physical activity participation in persons with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 63(12):1700–1705. doi:10.1002/acr.20616
Ehrlich-Jones L, Mallinson T, Fischer H, Bateman J, Semanik PA, Spring B, Ruderman E, Chang RW (2010) Increasing physical activity in patients with arthritis: a tailored health promotion program. Chronic Illn 6(4):272–281. doi:10.1177/1742395309351243
Shephard RJ (2003) Limits to the measurement of habitual physical activity by questionnaires. Br J Sports Med 37(3):197–206
Matthews CE, Hagstromer M, Pober DM, Bowles HR (2012) Best practices for using physical activity monitors in population-based research. Med Sci Sports Exerc 44(Suppl 1):S68–S76. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e3182399e5b
Prince SA, Adamo KB, Hamel ME, Hardt J, Connor Gorber S, Tremblay M (2008) A comparison of direct versus self-report measures for assessing physical activity in adults: a systematic review. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 5:56. doi:10.1186/1479-5868-5-56
van der Weijden MA, Claushuis TA, Nazari T, Lems WF, Dijkmans BA, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE (2012) High prevalence of low bone mineral density in patients within 10 years of onset of ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic review. Clin Rheumatol 31(11):1529–1535. doi:10.1007/s10067-012-2018-0
Fontaine KR, Bartlett SJ, Heo M (2005) Are health care professionals advising adults with arthritis to become more physically active? Arthritis Rheum 53(2):279–283. doi:10.1002/art.21073
Sanderson S, Tatt ID, Higgins JP (2007) Tools for assessing quality and susceptibility to bias in observational studies in epidemiology: a systematic review and annotated bibliography. Int J Epidemiol 36(3):666–676. doi:10.1093/ije/dym018
Deeks JJ, Dinnes J, D’Amico R, Sowden AJ, Sakarovitch C, Song F, Petticrew M, Altman DG (2003) Evaluating non-randomised intervention studies. Health Technol Assess 7(27):iii-x, 1–173
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank David Mockler (John Stearne Library, Trinity Centre for Health Sciences, Dublin 8) for his assistance in devising the electronic search strategy. TOD reports receipt of a studentship grant from Trinity College Dublin, during the conduct of the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O’Dwyer, T., O’Shea, F. & Wilson, F. Physical activity in spondyloarthritis: a systematic review. Rheumatol Int 35, 393–404 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-014-3141-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-014-3141-9