Abstract
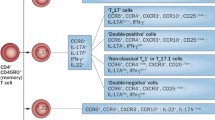
Th17 cells are a discrete subset of T cell subpopulation, which produce IL-17 and certain other pro-inflammatory cytokines. A regulatory role of Th17 cells have been proposed in several autoimmune diseases including psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis (PsA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, and multiple sclerosis. Psoriatic disease is an autoimmune disease which mainly involves skin and joints. Until recently, psoriasis and PsA were thought to be Th1 mediated disease, but after the discovery of IL-17 and IL-17 knockout animal studies as well as human experimental data indicate a crucial role of the Th17 cells in the pathogenesis of psoriasis and PsA. Our research group have not only found abundance of CD4+IL-17+ T cells, mainly the memory phenotype (CD4RO+CD45RA−CD11a+) in the synovial fluid, but also have shown the existence of a functional IL-17 receptor in synovial fibroblast of psoriatic arthritis patients. Similarly, both animal and human studies indicate a regulatory role of the Th17 cells in AS; most critical observations are that Th17 cytokines (IL-17 and IL-22) can contribute to bone erosion, osteitis and new bone formation the hall mark skeletal features associated with the pathophysiology of AS. In this review article, we have discussed the contributing role of the IL-23/IL-17 axis in the pathogenesis of PsA and AS.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appel H, Kuhne M, Spiekermann S, Ebhardt H, Grozdanovic Z, Köhler D, Dreimann M, Hempfing A, Rudwaleit M, Stein H, Metz-Stavenhagen P, Sieper J, Loddenkemper C (2006) Immunohistologic analysis of zygapophyseal joints in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum 54(9):2845–51
Lowes MA, Bowcock AM, Krueger JG (2007) Pathogenesis and therapy of psoriasis. Nature 445(7130):866–73
Raychaudhuri SP (2013) A cutting edge overview: psoriatic disease. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 44(2):109–13
Griffiths CE, Barker JN (2007) Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis. Lancet 370(9583):263–71
Liu Y, Krueger JG, Bowcock AM (2007) Psoriasis: genetic associations and immune system changes. Genes Immun 8(1):1–12
Gladman DD, Farwell VT, Pellett F, Schentag C, Raham P (2003) HLA is a candidate region for psoriatic arthritis. evidence for excessive HLA sharing in sibling pairs. Hum Immunol 64(9):887–9
Amherd-Hoekstra A, Naher H, Lorenz HM, Enk AH (2010) Psoriatic arthritis: a review. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 8(5):332–9
Raychaudhuri SP (2013) Role of IL-17 in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 44:183–93
Raychaudhuri SP, Jiang WY, Raychaudhuri SK (2008) Revisiting the Koebner phenomenon: role of NGF and its receptor system in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Am J Pathol 172(4):961–71
Raychaudhuri SP, Kundu-Raychaudhuri S, Tamura K, Masunaga T, Kubo K, Hanaoka K et al (2008) FR255734, a humanized, Fc-Silent, anti-CD28 antibody, improves psoriasis in the SCID mouse-psoriasis xenograft model. J Invest Dermatol 128(8):1969–76. doi:10.1038/jid.2008.38
Raychaudhuri SP, Mitra A, Datta Mitra A, Abria C, Raychaudhuri SK (2014) Th9 cells in inflammatory cascades of autoimmune arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 66(11):S708, Abstract 1602
Lowes MA, Russell CB, Martin DA, Towne JE, Krueger JG (2013) The IL-23/T17 pathogenic axis in psoriasis is amplified by keratinocyte responses. Trends Immunol 34(4):174–81
Kruithof E, Baeten D, Van den Bosch F, Mielants H, Veys EM, De Keyser F (2005) Histological evidence that infliximab treatment leads to downregulation of inflammation and tissue remodelling of the synovial membrane in spondyloarthropathy. Ann Rheum Dis 64:529–36
Raychaudhuri SP, Raychaudhuri SK (2004) Role of NGF and neurogenic inflammation in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Prog Brain Res 146:433–7
Elder JT, Bruce AT, Gudjonsson JE, Johnston A, Stuart PE, Tejasvi T et al (2010) Molecular dissection of psoriasis: integrating genetics and biology. J Invest Dermatol 130(5):1213–26
Chandran V, Raychaudhuri SP (2010) Geoepidemiology and environmental factors of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. J Autoimmun 34(3):J314–21
Bowes J, Orozco G, Flynn E, Ho P, Brier R, Marzo-Ortega H et al (2011) Confirmation of TNIP1 and IL23A as susceptibility loci for psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 70:1641–4
Filer C, Ho P, Smith RL, Griffiths C, Young HS, Worthington J et al (2012) Investigation of association of the IL12B and IL23R genes with psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 64(4):1302
Huffmeier U, Uebe S, Ekici AB, Bowes J, Giardina E, Korendowych E et al (2010) Common variants at TRAF3IP2 are associated with susceptibility to psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis. Nat Genet 42:996–9
WTCCC & TASC (2007) Association scan of 14,500 nonsynonymous SNPs in four diseases identifiesautoimmunity variants. Nat Genet 39:1329–1337
Mitra A, Raychaudhuri SK, Raychaudhuri SP (2012) Functional role of IL-22 in psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 14(2):R65
Lories RJ, McInnes IB (2012) Primed for inflammation: enthesis-resident T cells. Nat Med 18(7):1018–9
Baeten D, Braun J, Baraliakos X et al (2014) Secukinumab, a monoclonal antibody to interleukin-17A, significantly improves signs and symptoms of active ankylosing spondylitis: results of a 52-week phase 3 randomized placebo-controlled trial with intravenous loading and subcutaneous maintenance dosing. Arthritis Rheum 66:S360, Abstract 819
Sieper J, Braun J, Baraliakos X et al (2014) Secukinumab, a monoclonal antibody to interleukin-17A, significantly improves signs and symptoms of active ankylosing spondylitis: results of a phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled trial with subcutaneous loading and maintenance dosing. Arthritis Rheum 66:S232, Abstract 536
Mease PJ, Genovese MC, Greenwalk MW, Ritchlin CT, Beaulier AD, Deodhar A et al (2014) Brodalumab, an anti-IL17RA monoclonal antibody, in psoriatic arthritis. N Engl J Med 370(24):2295–306
Papp KA, Leonardi C, Menter A, Ortonne JP, Kreuger JG, Kricorian G et al (2012) Brodalumab, an anti-interleukin-17-receptor antibody for psoriasis. N Engl J Med 366(13):1181–9
Yao Z, Painter SL, Fanslow WC, Ulrich D, Macduff BM, Spriggs MK et al (1995) Human IL-17: a novel cytokine derived from T cells. J Immunol 155(12):5483–6
Tesmer LA, Lundy SK, Sarkar S, Fox DA (2008) Th17 cells in human disease. Immunol Rev 223:87–113
Kuestner RE, Taft DW, Haran A, Brandt CS, Brender T, Lum K et al (2007) Identification of the IL-17 receptor related molecule IL-17RC as the receptor for IL-17 F. J Immunol 179(8):5462–73
Liang SC, Long AJ, Bennett F, Whitters MJ, Karim R, Collins M et al (2007) An IL-17F/A heterodimer protein is produced by mouse Th17 cells and induces airway neutrophil recruitment. J Immunol 179(11):7791–9
Hymowitz SG, Filvaroff EH, Jp Y, Lee J, Cai L, Risser P et al (2001) IL-17s adopt a cystine knot fold: structure and activity of a novel cytokine, IL-17F, and implications for receptor binding. EMBO J 20(19):5332–41
Yao Z, Spriggs MK, Derry JM, Strockbine L, Park LS, Vanden Bos T et al (1997) Molecular characterization of the human interleukin (IL)-17 receptor. Cytokine 9(11):794–800
Ely LK, Fischer S, Garcia KC (2009) Structural basis of receptor sharing by interleukin 17 cytokines. Nat Immunol 10(12):1245–51
Toy D, Kugler D, Wolfson M, Vanden Bos T, Gurgel J, Derry J et al (2006) Cutting edge: interleukin 17 signals through a heteromeric receptor complex. J Immunol 177(1):36–9
Coimbra S, Figueriredo A, Castro E, Rocha-Pereira P, Santos-Silva A (2012) The roles of cells and cytokines in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Int J Dermatol 51(4):389–95, quiz 395-8
Lee E, Trepicchio WL, Oestreicher JL, Pittman D, Wang F, Chamian F et al (2004) Increased expression of interleukin 23 p19 and p40 in lesional skin of patients with psoriasis vulgaris. J Exp Med 199(1):125–30
Piskin G, Sylva-Steenland R, Bos JD, Teunissen MB (2006) In vitro and in situ expression of IL-23 by keratinocytes in healthy skin and psoriasis lesions: enhanced expression in psoriatic skin. J Immunol 176(3):1908–15
Bovenschen HJ, van de Kerkhof PC, van Erp PE, Woestenenk R, Joosten I, Koenen HJ (2011) Foxp3+ regulatory T cells of psoriasis patients easily differentiate into IL-17A-producing cells and are found in lesional skin. J Invest Dermatol 131(9):1853–60
Wilson NJ, Boniface K, Chan JR, McKenzie BS, Blumenschein W, Mattson JD et al (2007) Development, cytokine profile and function of human interleukin 17-producing helper T cells. Nat Immunol 8(9):950–7
Lowes MA, Kikuchi T, Fuentes-Duculan J, Cardinale I, Zaba LC, Haider AS et al (2008) Psoriasis vulgaris lesions contain discrete populations of Th1 and Th17 T cells. J Invest Dermatol 128(5):1207–11
Johansen C, Usher PA, Kjellerup RB, Lundsgaard D, Iversen L, Kragballe K (2009) Characterization of the interleukin-17 isoforms and receptors in lesional psoriatic skin. Br J Dermatol 160(2):319–24
van der Fits L, Mourits S, Voerman JS, Kant M, Boon L, Laman JD et al (2009) Imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice is mediated via the IL-23/IL-17 axis. J Immunol 182(9):5836–45
Homey B, Dieu-Nosjean MC, Wiesenborn A, Massacrier C, Pin JJ, Oldham E et al (2000) Up-regulation of macrophage inflammatory protein-3 alpha/CCL20 and CC chemokine receptor 6 in psoriasis. J Immunol 164(12):6621–32
Girolomoni G, Mrowietz U, Paul C (2012) Psoriasis: rationale for targeting interleukin-17. Br J Dermatol 167(4):717–24
Nograles KE, Zaba LC, Guttman-Yassky E, Fuentes-Duculan K, Suarex-Farinas M, Cardinale I et al (2008) Th17 cytokines interleukin (IL)-17 and IL-22 modulate distinct inflammatory and keratinocyte-response pathways. Br J Dermatol 159(5):1092–102
Liang SC, Tan XY, Luxenberg DP, Karim R, Dunussi-Joannopoulos K, Collins M et al (2006) Interleukin (IL)-22 and IL-17 are coexpressed by Th17 cells and cooperatively enhance expression of antimicrobial peptides. J Exp Med 203(10):2271–9
Gutowska-Owsiak D, Schaupp AL, Salimi M, Selvakumar TA, McPherson T, Taylor S et al (2012) IL-17 downregulates filaggrin and affects keratinocyte expression of genes associated with cellular adhesion. Exp Dermatol 21(2):104–10
Raychaudhuri SP, Raychaudhuri SK, Genovese MC (2012) IL-17 receptor and its functional significance in psoriatic arthritis. Mol Cell Biochem 359(1-2):419–29
Chabaud M, Lubberts E, Joosten L, van den Berg W, Miossec P (2001) IL-17 derived from juxta-articular bone and synovium contributes to joint degradation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res 3:168–177
Koshy PJ, Henderson N, Logan C, Life PF, Cawston TE, Rowan AD (2002) IL-17 induces cartilage collagen breakdown: novel synergistic effects in combination with proinflammatory cytokines. Ann Rheum Dis 61(8):704–713
Nakae S, Nambu A, Sudo K, Iwakura Y (2003) Suppression of immune induction of collagen-induced arthritis in IL-17-deficient mice. J Immunol 171(11):6173–6177
Koenders MI, Kolls JK, Oppers-Walgreen B, van den Bersselaar L, Joosten LA, Schurr JR et al (2005) Interleukin-17 receptor deficiency results in impaired synovial expression of interleukin-1 and matrix metalloproteinases 3, 9, and 13 and prevents cartilage destruction during chronic reactivated Streptococcal cell wall induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 52(10):3239–3247
Koenders MI, Lubberts E, Oppers-Walgreen B, van den Bersselaar L, Helsen MM, Di Padova FE et al (2005) Blocking of interleukin-17 during reactivation of experimental arthritis prevents joint inflammation and bone erosion by decreasing RANKL and interleukin-1. Am J Pathol 167(1):141–149
Kotake S, Udagawa N, Takahashi N, Matsuzaki K, Itoh K, Ishiyama S et al (1999) IL-17 in synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis is a potent stimulator of osteoclastogenesis. J Clin Invest 103(9):1345–1352
Australo-Anglo-American Spondyloarthritis Consortium (TASC), Reveille JD, Sims AM, Danoy P, Evans DM, Leo P, Pointon JJ et al (2010) Genome-wide association study of ankylosing spondylitis identifies non-MHC susceptibility loci. Nat Genet 42(2):123–127
Mei Y, Pan F, Gao J, Ge R, Duan Z, Zeng Z, Liao F, Xia G, Wang S, Xu S, Xu J, Zhang L, Ye D (2011) Increased serum IL-17 and IL-23 in the patient with ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Rheumatol 30:269–273
Zeng L, Lindstrom MJ, Smith JA (2011) Ankylosing spondylitis macrophage production of higher levels of interleukin-23 in response to lipopolysaccharide. Arthritis Rheum 63(12):3807–17
Appel H, Maier R, Wu P, Scheer R, Hempfing A, Kayser R, Thiel A, Radbruch A, Loddenkemper C, Sieper J (2011) Analysis of IL-17(+) cells in facet joints of patients with spondyloarthritis suggests that the innate immune pathway might be of greater relevance than the Th17-mediated adaptive immune response. Arthritis Res Ther 13:R95
Singh AK, Misra R, Aggarwal A (2011) Th17 associated cytokines in patients with reactive arthritis/undifferentiated spondylarthropathy. Clin Rheumatol 30:771–776
Ritchlin CT, Haas-Smith SA, Li P, Hicks DG, Schwarz EM (2003) Mechanisms of TNF-alpha- and RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption in psoriatic arthritis. J Clin Invest 111(6):821–31
Sherlock JP, Joyce-Shaikh B, Turner SP et al (2012) IL-23 induces spondyloarthropathy by acting on ROR-gammatþ CD3þCD4-CD8- entheseal resident T cells. Nat Med 18:1069–1076
Disclaimer
The views expressed in the article do not necessarily represent the views of the Department of Veterans Affairs or of the United States Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raychaudhuri, S.K., Saxena, A. & Raychaudhuri, S.P. Role of IL-17 in the pathogenesis of psoriatic arthritis and axial spondyloarthritis. Clin Rheumatol 34, 1019–1023 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-015-2961-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-015-2961-7