Abstract
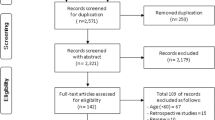
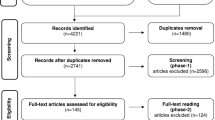
The study aimed to determine, using systematic review and meta-analysis, the level of evidence supporting the construct validity of spinal mobility tests for assessing patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Following the guidelines proposed in the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses, three sets of keywords were used for data searching: (i) ankylosing spondylitis, spondyloarthritis, spondyloarthropathy, spondylarthritis; (ii) accuracy, association, construct, correlation, Outcome Measures in Rheumatoid Arthritis Clinical Trials, OMERACT, truth, validity; (iii) mobility, Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Metrology Index—BASMI, radiography, spinal measures, cervical rotation, Schober (a further 19 keywords were used). Initially, 2558 records were identified, and from these, 21 studies were retained. Fourteen of these studies were considered high level of evidence. Compound indexes of spinal mobility showed mostly substantial to excellent levels of agreement with global structural damage. Individual mobility tests for the cervico-thoracic spine showed only moderate agreements with cervical structural damage, and considering structural damage at the lumbar spine, the original Schober was the only test that presented consistently substantial levels of agreement. Three studies assessed the construct validity of mobility measures for inflammation and low to fair levels of agreement were observed. Two meta-analyses were conducted, with assessment of agreement between BASMI and two radiological indexes of global structural damage. The spinal mobility indexes and the original Schober test show acceptable construct validity for inferring the extent of structural damage when assessing patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Spinal mobility measures do not reflect levels of inflammation at either the sacroiliac joints and/or the spine.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dean LE, Jones GT, MacDonald AG, Downham C, Sturrock RD, Macfarlane GJ (2014) Global prevalence of ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatology 53:650–657
van der Linden S, Valkenburg H, Cats A (1984) Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum 27:361–368
Bennett AN, McGonagle D, O’Connor P et al (2008) Severity of baseline magnetic resonance imaging-evident sacroiliitis and HLA-B27 status in early inflammatory back pain predict radiographically evident ankylosing spondylitis at eight years. Arthritis Rheum 58:3413–3418
Oostveen J, Prevo R, den Boer J, van de Laar M (1999) Early detection of sacroiliitis on magnetic resonance imaging and subsequent development of sacroiliitis on plain radiography. A prospective, longitudinal study. J Rheumatol 26:1953–1958
Rudwaleit M, Jurik AG, Hermann K-GA et al (2009) Defining active sacroiliitis on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for classification of axial spondyloarthritis: a consensual approach by the ASAS/OMERACT MRI group. Ann Rheum Dis 68:1520–1527
Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Landewé R et al (2009) The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part II): validation and final selection. Ann Rheum Dis 68:777–783
Rudwaleit M, Landewé R, van der Heijde D et al (2009) The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part I): classification of paper patients by expert opinion including uncertainty appraisal. Ann Rheum Dis 68:770–776
Bakland G, Nossent H (2013) Epidemiology of Spondyloarthritis: a review. Curr Rheumatol Rep 15:1–7
Van Der Heijde D, Calin A, Dougados M, Khan MA, Van Der Linden S, Bellamy N (1999) Selection of instruments in the core set for DC-ART, SMARD, physical therapy, and clinical record keeping in ankylosing spondylitis. Progress report of the ASAS Working Group. J Rheumatol 26:951–954
Brandt J, Listing J, Sieper J, Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Braun J (2004) Development and preselection of criteria for short term improvement after anti-TNF alpha treatment in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 63:1438–1444
Davis JC, Gladman DD (2007) Spinal mobility measures in spondyloarthritis: application of the OMERACT filter. J Rheumatol 34:666–670
Portney LG, Watkins MP (2009) Foundations of clinical research: applications to practice, 3rd edn. Pearson & Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Castro MP, Stebbings SM, Milosavljevic S, Bussey M (2015) Criterion-concurrent validity of spinal mobility tests in ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic review of the literature. J Rheumatol 42:243–251
Jenkinson T, Mallorie P, Whitelock H, Kennedy L, Garrett S, Calin A (1994) Defining spinal mobility in ankylosing spondylitis (AS). The Bath AS Metrology Index. J Rheumatol 21:1694–1698
Maksymowych WP, Mallon C, Richardson R et al (2006) Development and validation of the Edmonton Ankylosing Spondylitis Metrology Index. Arthritis Care Res 55:575–582
Howick J, Chalmers I, Glasziou P et al (2011) The 2011 Oxford CEBM Evidence Levels of Evidence (Introductory Document)
Garrido-Castro JL, Escudero A, Medina-Carnicer R et al (2014) Validation of a new objective index to measure spinal mobility: the University of Cordoba Ankylosing Spondylitis Metrology Index (UCOASMI). Rheumatol Int 34:401–406
Dale K, Vinje O (1985) Radiography of the spine and sacro-iliac joints in ankylosing spondylitis and psoriasis. Acta Radiol Diagn 26:145–159
MacKay K, Mack C, Brophy S, Calin A (1998) The Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Radiology Index (BASRI): a new, validated approach to disease assessment. Arthritis Rheum 41:2263–2270
Taylor HG, Wardle T, Beswick EJ, Dawes PT (1991) The relationship of clinical and laboratory measurements to radiological change in ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatology 30:330–335
Creemers MC, Franssen MJ, van ’t Hof MA, Gribnau FW, van de Putte LB, van Riel PL (1993) A radiographic scoring system and identification of variables measuring structural damage in ankylosing spondylitis. University of Nijmegen, Nijmegen
Braun J, Baraliakos X, Golder W et al (2003) Magnetic resonance imaging examinations of the spine in patients with ankylosing spondylitis, before and after successful therapy with infliximab: evaluation of a new scoring system. Arthritis Rheum 48:1126–1136
Lukas C, Braun J, van der Heijde D et al (2007) Scoring inflammatory activity of the spine by magnetic resonance imaging in ankylosing spondylitis: a multireader experiment. J Rheumatol 34:862–870
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med 151:264–269
Whiting P, Rutjes A, Reitsma J, Bossuyt P, Kleijnen J (2003) The development of QUADAS: a tool for the quality assessment of studies of diagnostic accuracy included in systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol 3:25
Cho H, Kim T, Kim TH, Lee S, Lee KH (2013) Spinal mobility, vertebral squaring, pulmonary function, pain, fatigue, and quality of life in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rehabil Med 37:675–682
Konca S, Keskin D, Ciliz D, Bodur H, Sakman B (2012) Spinal inflammation by magnetic resonance imaging in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: association with disease activity and outcome parameters. Rheumatol Int 32:3765–3770
Yacoub YI, Amine B, Laatiris A, Abouqal R, Hajjaj-Hassouni N (2011) Spinal mobility and its impact in Moroccan patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Rheumatol 30:239–243
Machado P, Landewe R, Braun J, Hermann KG, Baker D, van der Heijde D (2010) Both structural damage and inflammation of the spine contribute to impairment of spinal mobility in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 69:1465–1470
Rudwaleit M, Schwarzlose S, Hilgert ES, Listing J, Braun J, Sieper J (2008) MRI in predicting a major clinical response to anti-tumour necrosis factor treatment in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 67:1276–1281
Salaffi F, Carotti M, Garofalo G, Giuseppetti GM, Grassi W (2007) Radiological scoring methods for ankylosing spondylitis: a comparison between the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Radiology Index and the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score. Clin Exp Rheumatol 25:67–74
Chandran V, O’Shea FD, Schentag CT, Inman RD, Gladman DD (2007) Relationship between spinal mobility and radiographic damage in ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic spondylitis: a comparative analysis. J Rheumatol 34:2463–2465
Kaya T, Gelal F, Gunaydin R (2006) The relationship between severity and extent of spinal involvement and spinal mobility and physical functioning in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Rheumatol 25:835–839
Wanders A, Landewe R, Dougados M, Mielants H, van der Linden S, van der Heijde D (2005) Association between radiographic damage of the spine and spinal mobility for individual patients with ankylosing spondylitis: can assessment of spinal mobility be a proxy for radiographic evaluation? Ann Rheum Dis 64:988–994
Baraliakos X, Listing J, Rudwaleit M, Brandt J, Sieper J, Braun J (2005) Radiographic progression in patients with ankylosing spondylitis after 2 years of treatment with the tumour necrosis factor a antibody infliximab. Ann Rheum Dis 64:1462–1466
Wanders AJB, Landewé RBM, Spoorenberg A et al (2004) What is the most appropriate radiologic scoring method for ankylosing spondylitis? Arthritis Rheum 50:2622–2632
Ozgocmen S, Ardicoglu O, Kaya A (2000) The relationship of clinical and laboratory measurements to two different radiological scoring methods in ankylosing spondylitis. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil 15:37–40
Viitanen JV, Heikkila S, Kokko ML, Kautiainen H (2000) Clinical assessment of spinal mobility measurements in ankylosing spondylitis: a compact set for follow-up and trials? Clin Rheumatol 19:131–137
Viitanen JV, Kokko ML, Heikkila S, Kautiainen H (1998) Neck mobility assessment in ankylosing spondylitis: a clinical study of nine measurements including new tape methods for cervical rotation and lateral flexion. Br J Rheumatol 37:377–381
Viitanen JV, Kokko ML, Heikkila S, Kautiainen H (1999) Assessment of thoracolumbar rotation in ankylosing spondylitis: a simple tape method. Clin Rheumatol 18:152–157
Viitanen JV, Kautiainen H, Suni J, Kokko ML, Lehtinen K (1995) The relative value of spinal and thoracic mobility measurements in ankylosing spondylitis. Scand J Rheumatol 24:94–97
Viitanen JV, Kokko ML, Lehtinen K, Suni J, Kautiainen H (1995) Correlation between mobility restrictions and radiologic changes in ankylosing spondylitis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 20:492–496
Kennedy LG, Jenkinson TR, Mallorie PA, Whitelock HC, Garrett SL, Calin A (1995) Ankylosing spondylitis: the correlation between a new metrology score and radiology. Br J Rheumatol 34:767–770
Viitanen JV (1993) Thoracolumbar rotation in ankylosing spondylitis: a new noninvasive measurement method. Spine 18:880–883
Williams R, Goldsmith C, Minuk T (1998) Validity of the double inclinometer method for measuring lumbar flexion. Physiother Can 50:147–152
Batti’e MC, Bigos SJ, Sheehy A, Wortley MD (1987) Spinal flexibility and individual factors that influence it. Phys Ther 67:653–658
Cook CE, Wilhelm M, Cook AE, Petrosino C, Isaacs R (2011) Clinical tests for screening and diagnosis of cervical spine myelopathy: a systematic review. J Manip Physiol Ther 34:539–546
Rezvani A, Ergin O, Karacan I, Oncu M (2012) Validity and reliability of the metric measurements in the assessment of lumbar spine motion in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Spine 37:1189–1196
Disclosures
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castro, M.P., Stebbings, S.M., Milosavljevic, S. et al. Construct validity of clinical spinal mobility tests in ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rheumatol 35, 1777–1787 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-015-3056-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-015-3056-1