Abstract
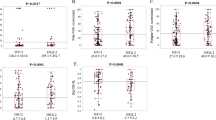
This study aimed to assess the responsiveness of ultrasonography (US)-7 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Eighty-two RA patients were recruited and followed up for 22 weeks. The clinical, laboratory, and X-ray assessments, along with grayscale US (GSUS) and power Doppler US (PDUS) examinations were performed at baseline, 6, 14, and 22 weeks after infliximab treatment. GSUS for synovitis and PDUS for synovitis and paratendinitis/tenosynovitis were assessed by a semi-quantitative (0 to 3) score, while GSUS for paratendinitis/tenosynovitis and bone erosion was qualitatively assessed as absent or present (0 or 1). US scores in both 7-joint (US7) and 12-joint (US12) systems were evaluated. After 6, 14, and 22 weeks of treatment with infliximab, indices such as US scores, 28-joint disease activity (DAS28) score, and tender and swelling joint count were all significantly improved compared to baseline. US7 scores were significantly correlated with that of US12. Strong correlations were identified between most US7 scores with DAS28, health assessment questionnaire (HAQ), and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels. When DAS28 was used as a reference, the US7 cutoff for disease remission was less than 35 for GS + PD and also less than 29 for GS and 1 for PD, respectively. Additionally, the positive percent agreement, negative percent agreement, and overall percent agreement for GS + PD were 77.78, 76.19, and 76.67 %, respectively, which were all higher than that of GS or PD. US7 may be a feasible tool to assess the therapeutic response in RA patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Camussi G, Lupia E (1998) The future role of anti-tumour necrosis factor (TNF) products in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Drugs 55:613–620
Gravallese EM, Goldring SR (2000) Cellular mechanisms and the role of cytokines in bone erosions in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 43:2143–2151
Shanahan JC, StClair W (2002) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha blockade: a novel therapy for rheumatic disease. Clin Immunol 103:231–242
Maini RN, Breedveld FC, Kalden JR et al (2004) Sustained improvement over two years in physical function, structural damage, and signs and symptoms among patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with infliximab and methotrexate. Arthritis Rheum 50:1051–1065
StClair EW, Van Der Heijde DM, Smolen JS et al (2004) Combination of infliximab and methotrexate therapy for early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 50:3432–3443
Prevoo ML, Van’T Hof MA, Kuper HH, Van Leeuwen MA, Van De Putte LB, Van Riel PL (1995) Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight joint counts: development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 38:44–48
Conaghan PG, O’connor P, Mcgonagle D et al (2003) Elucidation of the relationship between synovitis and bone damage: a randomized magnetic resonance imaging study of individual joints in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 48:64–71
Backhaus M, Kamradt T, Sandrock D et al (1999) Arthritis of the finger joints: a comprehensive approach comparing conventional radiography, scintigraphy, ultrasound, and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Arthritis Rheum 42:1232–1245
Szkudlarek M, Narvestad E, Klarlund M, Court-PayenM THS, Østergaard M (2004) Ultrasonography of the metatarsophalangeal joints in rheumatoid arthritis: comparison with magnetic resonance imaging, conventional radiography, and clinical examination. Arthritis Rheum 50:2103–2112
Schmidt WA, Völker L, Zacher J, Schläfke M, Ruhnke M, Gromnica-Ihle E (2000) Colour Doppler ultrasonography to detect pannus in knee joint synovitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 18:439–444
Walther M, Harms H, Krenn V, Radke S, Faehndrich TP, Gohlke F (2001) Correlation of power Doppler sonography with vascularity of the synovial tissue of the knee joint in patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 44:331–338
Walther M, Harms H, Krenn V, Radke S, Kirschner S, Gohlke F (2002) Synovial tissue of the hip at power Doppler US: correlation between vascularity and power Doppler US signal. Radiology 225:225–231
Szkudlarek M, Strandberg C, Court-Payen M, Klarlund M, Klausen T, Ostergaard M (2001) Power Doppler ultrasonography for assessment of synovitis in the metacarpophalangeal joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a comparison with dynamic magnetic resonance imaging. Arthritis Rheum 44:2018–2023
Terslev L, Torp-Pedersen S, Savnik A et al (2003) Doppler ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging of synovial inflammation of the hand in rheumatoid arthritis: a comparative study. Arthritis Rheum 48:2434–2441
Taylor PC, Steuer A, Gruber J et al (2004) Comparison of ultrasonographic assessment of synovitis and joint vascularity with radiographic evaluation in a randomized, placebo-controlled study of infliximab therapy in early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 50:1107–1116
Filippucci E, Farina A, Carotti M, Salaffi F, Grassi W (2004) Grey scale and power Doppler sonographic changes induced by intra-articular steroid injection treatment. Ann Rheum Dis 63:740–743
Naredo E, Bonilla G, Gamero F, Laffon A (2005) Assessment of inflammatory activity in rheumatoid arthritis: a comparative study of clinical evaluation with gray-scale and power Doppler ultrasonography. Ann Rheum Dis 64:375–381
Backhaus M, Ohrndorf S, Kellner H et al (2009) Evaluation of a novel 7-joint ultrasound score in daily rheumatologic practice: a pilot project. Arthritis Rheum 61:1194–1201
Arnett FC, Edwarthy SM, Bloch DA et al (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31:315–324
Van der Heijde D, Boers M, Boonen A, Kostense P, van der Linden S (1999) Reading radiographs in chronological order, in pairs or as single films has important implications for the discriminative power of rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials. Rheumatology (Oxford) 38:1213–1220
Van der Heijde D (2000) How to read radiographs according to the Sharp/van der Heijde method. J Rheumatol 27:261–263
Backhaus M, Burmester GR, Gerber T et al (2001) Guidelines for musculoskeletal ultrasound in rheumatology. Ann Rheum Dis 60:641–649
Naredo E, Rodríguez M, Campos C et al (2008) Validity, reproducibility, and responsiveness of a twelve-joint simplified power Doppler ultrasonographic assessment of joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 59:515–522
Hammer HB, Kvien TK (2011) Comparisons of 7- to 78-joint ultrasonography scores: all different joint combinations show equal response to adalimumab treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 27;13:R78
Cicchetti DV, Feinstein AR (1990) High agreement but low kappa: II. Resolving the paradoxes. J Clin Epidemiol 43:551–558
Ribbens C, André B, Marcelis S et al (2003) Rheumatoid hand joint synovitis: gray-scale and power Doppler US quantifications following anti-tumor necrosis factor-α treatment: pilot study. Radiology 229:562–569
Newman JS, Laing TJ, McCarthy TJ, Adler RS (1996) Power Doppler sonography of synovitis: assessment of therapeutic response: preliminary observations. Radiology 198:582–584
Hau M, Schultz H, Tony HP et al (1999) Evaluation of pannus and vascularization of the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints in rheumatoid arthritis by high-resolution ultrasound (multidimensional linear array). Arthritis Rheum 42:2303–2308
Terslev L, Torp-Pedersen S, Qvistgaard E, Danneskiold-Samsoe B, Bliddal H (2003) Estimation of inflammation by Doppler ultrasound: quantitative changes after intra-articular treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 62:1049–1053
Koski JM, Saarakkala S, Helle M, Hakulinen U, Hermunen H (2006) Power Doppler ultrasonography and synovitis: correlating ultrasound imaging with histopathological findings and evaluating the performance of ultrasound equipments. Ann Rheum Dis 65:1590–1595
Dougados M, Jousse-Joulin S, Mistretta F et al (2010) Evaluation of several ultrasonography scoring systems of synovitis and comparison to clinical examination: results from a prospective multi-center study of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 69:828–833
Gardiner PV, Bell AL, Taggart AJ et al (2005) A potential pitfall in the use of the disease activity score (DAS 28) as the main response criterion in the treatment guidelines for patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 64:506–507
Fransen J, Creemers MC, Van Riel PL (2004) Remission in rheumatoid arthritis: agreement of the disease activity score (DAS28) with the ARA preliminary remission criteria. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43:1252–1255
Ben Abdelghani K, Miladi S, Souabni L et al (2015) Role of ultrasound in assessing remission in rheumatoid arthritis. Diagn Interv Imaging 96:3–10
Prevoo ML, van Gestel AM, van Hof MA, van Rijswijk MH, van de Putte LB, van Riel PL (1996) Remission in a prospective study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. American Rheumatism Association preliminary remission criteria in relation to the disease activity score. Br J Rheumatol 35:1101–1105
Backhaus TM, Ohrndorf S, Kellner H et al (2013) The US7 score is sensitive to change in a large cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis over 12 months of therapy. Ann Rheum Dis 72:1163–1169
Ohrndorf S, Fischer IU, Kellner H et al (2012) Reliability of the novel 7-joint ultrasound score: results from an inter- and intraobserver study performed by rheumatologists. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 64:1238–1243
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Yuepeng Guo and Zhijing Qian for their enormous medical support and collaboration while working at the Medical Affairs Department of China Janssen. Both gave professional suggestions regarding this study and publication. Janssen China provided financial support for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study (trial number: NCT01282528) was approved by the local ethics committee, and all eligible patients provided signed informed consent.
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Xiaomei Leng, Weiguo Xiao and Zhonghui Xu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leng, X., Xiao, W., Xu, Z. et al. Ultrasound7 versus ultrasound12 in monitoring the response to infliximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 35, 587–594 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-016-3176-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-016-3176-2