Abstract
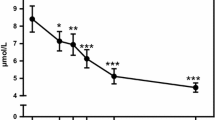
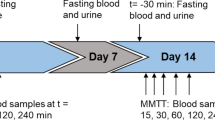
To characterize daily variation of amino acids (AAs) and acylcarnitines (ACs) in response to feeding and activity, we measured serum metabolites at various times and after various activities during the day. Subjects were admitted overnight for serial serum sampling, collected in the evening (6–8 p.m., n = 40), before rising from bed or eating (8 a.m., n = 40), 1 h after rising but before eating (9 a.m., n = 20), 1–2 h after rising and breakfast (9–10 a.m., n = 40), and at noon (12 p.m., n = 20). Measurements of 15 AAs and 45 ACs were performed by quantitative tandem mass spectrometry using stable-isotope dilution. Coefficients of variation within and between patients were calculated for individual metabolite values and factors derived from principal components analysis. The change of state between timepoints was evaluated by nearest neighbor non-parametric analysis of values at one timepoint compared to the next subsequent value. Relative to baseline a.m. recumbent concentrations, AA concentrations rose after activity and feeding while AC concentrations rose after activity and decreased with feeding. Furthermore, for all AAs, ACs, and their factors, biological variation was quantifiably evident and distinct from daily variation. This study confirms the daily variation of AAs and provides the first report of daily variation for a large panel of ACs. Although standardization of sample collection is highly desirable to control for daily variation (within a subject due to activity or feeding), this study demonstrated measurable biological variability (across subjects) suggesting that non-standardized sample collections could potentially provide insights into specific AA and AC metabolic pathways and disease mechanisms.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AC:
-
Acylcarnitine
- AA:
-
Amino acid
- CV:
-
Coefficient of variation
- FA:
-
Fatty acids
- LLOQ:
-
Lower limit of quantification
- MS:
-
Mass spectrometry
- OA:
-
Osteoarthritis
- PCA:
-
Principal components analysis
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
References
An, J., Muoio, D. M., Shiota, M., et al. (2004). Hepatic expression of malonyl-CoA decarboxylase reverses muscle, liver and whole-animal insulin resistance. Nature Medicine, 10, 268–274.
Bain, J. R., Stevens, R. D., Wenner, B. R., Ilkayeva, O., Muoio, D. M., & Newgard, C. B. (2009). Metabolomics applied to diabete research: Moving from information to knowledge. Diabetes, 58(11), 2429–2443.
Chace, D. H., Hillman, S. L., Millington, D. S., et al. (1995). Rapid dignosis of maple syrup urine disease in blood spots from newborns by tandem mass spectrometry. Clinical Chemistry, 41, 62–68.
Chace, D. H., Millington, D. S., Terada, N., et al. (1993). Rapid diagnois of phenylketonuria by quantitative analysis for phenylalanine and tyrosine in neonatal blood spots by tandem mass spectrometry. Clinical Chemistry, 39, 66–71.
Criscione, L. G., Elliott, A. L., Stabler, T. V., Jordan, J. M., Pieper, C. F., & Kraus, V. B. (2005). Variation of serum hyaluronan with activity in individuals with knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage, 13, 837–840.
De Jesus, V. R., Chace, D. H., Lim, T. H., Mei, J. V., & Hannon, W. H. (2010). Comparison of amino acids and acylcarnitines assay methods used in newborn screening assays by tandem mass spectrometry. Clinica Chimica Acta, 411, 684–689.
Eriksson, T., Voog, L., Walinder, J., & Eriksson, T. E. (1989). Diurnal rhythm in absolute and relative concentrations of large neutral amino acids in human plasma. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 23(3/4), 241–249.
Feigin, R. D., Klainer, A. S., & Beisel, W. R. (1967). Circadian periodicity of blood amino-acids in adult man. Nature, 215, 512–514.
Feigin, R. D., Klainer, A. S., & Beisel, W. R. (1968). Factors affecting circadian periodicity of blood amino acids in man. Metabolism, 17(9), 764–775.
Gabriel, S. E., & Michaud, K. (2009). Epidemiological studies in incidence, prevalence, mortality, and co-morbidity of the rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Research and Therapy, 11, 229.
Galgani, J. E., Moro, C., & Ravussin, E. (2008). Metabolic flexibility and insulin resistance. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism, 295, E1009–E1017.
Gordon, C. D., Stabler, T. V., & Kraus, V. B. (2008). Variation in osteoarthritis biomarkers from activity not food consumption. Clinica Chimica Acta, 398, 21–26.
Huffman, K. M., Shah, S. H., Bain, J. R., et al. (2009). Relationships between circulating metabolic intermediates and insulin action in overweight to obese, inactive men and women. Diabetes Care, 32(9), 1678–1683.
Lawrence, R. C., Felson, D. T., Helmick, C. G., et al. (2008). Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the United States. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 58(1), 26–35.
Lum, H., Sloane, R., Huffman, K. M., et al. (2011). Plasma acylcarnitines are associated with physical performance in elderly men. Journal of Gerontology Medical Sciences, 66A(5), 548–553.
Maher, T. J., Glaeser, B. S., & Wurtman, R. J. (1984). Diurnal variations in plasma concentrations of basic and neutral amino acids and in red cell concentrations of aspartate and glutamate: Effects of dietary protein intake. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 39, 722–729.
Millington, D. S., & Chace, D. H. (1992). Carnitine and acylcarnitines in metabolic disease diagnosis and management. In D. M. Desiderio (Ed.), Mass spectrometry: Clinical and biomedical applications (pp. 199–219). New York: Plenum Press.
Millington, D. S., & Stevens, R. D. (2011). Acylcarnitines: Analysis in plasma and whole blood using tandem mass spectrometry. Methods in Molecular Biology, 708, 55–72.
Newgard, C. B., An, J., Bain, J. R., et al. (2009). A branched-chain amino acid-related metabolic signature that differentiates obese and lean humans and contributes to insulin resistance. Cell Metabolism, 9, 311–326.
Oakman, C., Tenori, L., Biganzoli, L., et al. (2011). Uncovering the metabolic fingerprint of breast cancer. International Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, 43(7), 1010–1020.
Park, Y., Kim, S. B., Wang, B., et al. (2009). Individual vriation in macronutrient regulation measured by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of human plasma. American Journal of Physiology: Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 297, R202–R209.
Redman, L. M., Huffman, K. M., Landerman, L. R., et al. (2011). Effect of caloric restriction with and without exercise on metabolic intermediates in nonobese men and women. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 96(2), E312–E321.
Shah, S. H., Bain, J. R., Muehlbauer, M. J., et al. (2010). Association of a peripheral blood metabolic profile with corony artery disease and risk of subsequent cardiovascular events. Circulation: Cardiovascular Genetics, 3, 207–214.
Shah, S. H., Hauser, E. R., Bain, J. R., et al. (2009). High heritability of metabolimic profiles in families burdened with premature cardiovascular disease. Molecular Systems Biology, 5, 258.
Slupsky, C. M., Rankin, K. N., Wagner, J., et al. (2007). Investigations of the effects of gender, diurnal variation, and age in human urinary metabolomic profiles. Analytical Chemistry, 79(18), 6995–7004.
Vinayavekhin, N., Homan, E. A., & Saghatelian, A. (2010). Exploring disease through metabolomics. ACS Chemical Biology, 5(1), 91–103.
Wu, J. Y., Kao, H. J., Li, et al. (2004). ENU mutagenesis identifies mice with mitochondrial branched-chain aminotransferase deficiency resembling human maple syrup urine disease. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 113, 434–440.
Acknowledgments
We are appreciative of the time contributed by study participants. This study was supported by the National Institute on Aging at the National Institutes of Health (Claude D. Pepper Older Americans Independence Centers 5P30 AG028716): National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases at the National Institutes of Health (RO1 AR48769): and the National Center for Research Resources at the National Institutes of Health (MO1-RR-30), supporting the Duke General Clinical Unit where this study was conducted.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thompson, D.K., Sloane, R., Bain, J.R. et al. Daily variation of serum acylcarnitines and amino acids. Metabolomics 8, 556–565 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-011-0345-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-011-0345-9