Abstract
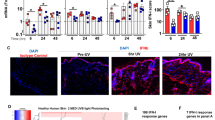
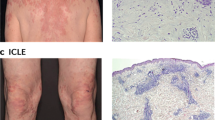
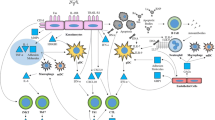
The underlying pathomechanisms of lupus erythematosus (LE), a multifactorial autoimmune disease, remain elusive. Due to the clinical evidence demonstrating a clear relationship between ultraviolet (UV) light exposure and skin lesions of LE, photosensitivity has been proven to be an important factor in the pathogenesis of the disease. Standardised photoprovocation with UVA and UVB irradiation has been shown to be a reliable model for evaluating photosensitivity in patients with cutaneous LE (CLE) and analysing the underlying medical conditions of the disease. In this respect, UV irradiation can cause aberrant induction of apoptosis in keratinocytes and contribute to the appearance of excessive apoptotic cells in the skin of CLE patients. Moreover, apoptotic cells that cannot be cleared by phagocytes may undergo secondary necrosis and release proinflammatory compounds and potential autoantigens, which may contribute to the inflammatory micromilieu that leads to formation of skin lesions in the disease. In addition to UV-mediated induction of apoptosis, the molecular and cellular factors that may cause the abnormal long-lasting photoreactivity in CLE include mediators of inflammation, such as cytokines and chemokines. In particular, interferons (IFNs) are important players in the early activation of the immune system and have a specific role in the immunological interface between the innate and the adaptive immune system. The fact that treatment with recombinant type I IFNs (α and β) can induce not only systemic organ manifestations but also LE-like skin lesions provides additional evidence for a pathogenetic role of these IFNs in the disease.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gilliam JN, Sontheimer RD (1981) Distinctive cutaneous subsets in the spectrum of lupus erythematosus. J Am Acad Dermatol 4:471–475
Provost TT (2004) Nonspecific cutaneous manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. In: Kuhn A, Lehmann P, Ruzicka T (eds) Cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 93–106
Schmitt V, Meuth AM, Amler S, Kuehn E, Haust M, Messer G et al (2010) Lupus erythematosus tumidus is a separate subtype of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Br J Dermatol 162:64–73
Kuhn A, Bein D, Bonsmann G (2009) The 100th anniversary of lupus erythematosus tumidus. Autoimmun Rev 8:441–448
Kuhn A, Ruzicka T (2004) Classification of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. In: Kuhn A, Lehmann P, Ruzicka T (eds) Cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Springer, Berlin, pp 53–58
Kim A, Chong BF (2013) Photosensitivity in cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 29:4–11
Kuhn A, Ruland V, Bonsmann G (2010) Photosensitivity, phototesting, and photoprotection in cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Lupus 19:1036–1046
Foering K, Chang AY, Piette EW, Cucchiara A, Okawa J, Werth VP (2013) Characterization of clinical photosensitivity in cutaneous lupus erythematosus. J Am Acad Dermatol 69:205–213
Kuhn A, Sonntag M, Richter-Hintz D, Oslislo C, Megahed M, Ruzicka T et al (2001) Phototesting in lupus erythematosus: a 15-year experience. J Am Acad Dermatol 45:86–95
Schmidt E, Tony HP, Brocker EB, Kneitz C (2007) Sun-induced life-threatening lupus nephritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1108:35–40
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, Masi AT, McShane DJ, Rothfield NF et al (1982) The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 25:1271–1277
Hochberg MC (1997) Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40:1725
Nyberg F, Hasan T, Puska P, Stephansson E, Hakkinen M, Ranki A et al (1997) Occurrence of polymorphous light eruption in lupus erythematosus. Br J Dermatol 136:217–221
Albrecht J, Berlin JA, Braverman IM, Callen JP, Connolly MK, Costner MI et al (2004) Dermatology position paper on the revision of the 1982 ACR criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 13:839–849
Petri M, Orbai AM, Alarcon GS, Gordon C, Merrill JT, Fortin PR et al (2012) Derivation and validation of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 64:2677–2686
Kuhn A, Beissert S (2005) Photosensitivity in lupus erythematosus. Autoimmunity 38:519–529
Epstein JH, Tuffanelli D, Dubois EL (1965) Light sensitivity and lupus erythematosus. Arch Dermatol 91:483–485
Cripps DJ, Rankin J (1973) Action spectra of lupus erythematosus and experimental immunofluorescence. Arch Dermatol 107:563–567
Freeman RG, Knox JM, Owens DW (1969) Cutaneous lesions of lupus erythematosus induced by monochromatic light. Arch Dermatol 100:677–682
Lehmann P, Hölzle E, von Kries R, Plewig G (1986) Lichtdiagnostische Verfahren bei Patienten mit Verdacht auf Photodermatosen. ZentrBl HuG 152:667–682
Lehmann P, Hölzle E, Kind P, Goerz G, Plewig G (1990) Experimental reproduction of skin lesions in lupus erythematosus by UVA and UVB radiation. J Am Acad Dermatol 22:181–187
Klein RS, Werth VP, Dowdy JC, Sayre RM (2009) Analysis of compact fluorescent lights for use by patients with photosensitive conditions. Photochem Photobiol 85:1004–1010
Klein RS, Sayre RM, Dowdy JC, Werth VP (2009) The risk of ultraviolet radiation exposure from indoor lamps in lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun Rev 8:320–324
Kuhn A, Wozniacka A, Szepietowski JC, Glaser R, Lehmann P, Haust M et al (2011) Photoprovocation in cutaneous lupus erythematosus: a multicenter study evaluating a standardized protocol. J Investig Dermatol 131:1622–1630
Ruland V, Haust M, Stilling RM, Amler S, Ruzicka T, Kuhn A (2013) Updated analysis of standardised photoprovocation in patients with cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Care Res 65:767–776
Vaux DL, Korsmeyer SJ (1999) Cell death in development. Cell 96:245–254
Henson PM, Hume DA (2006) Apoptotic cell removal in development and tissue homeostasis. Trends Immunol 27:244–250
Orrenius S (2007) Reactive oxygen species in mitochondria-mediated cell death. Drug Metab Rev 39:443–455
Fadok VA, Voelker DR, Campbell PA, Cohen JJ, Bratton DL, Henson PM (1992) Exposure of phosphatidylserine on the surface of apoptotic lymphocytes triggers specific recognition and removal by macrophages. J Immunol 148:2207–2216
Wyllie AH, Kerr JF, Currie AR (1980) Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol 68:251–306
Nagata S, Hanayama R, Kawane K (2010) Autoimmunity and the clearance of dead cells. Cell 140:619–630
Parnaik R, Raff MC, Scholes J (2000) Differences between the clearance of apoptotic cells by professional and non-professional phagocytes. Curr Biol 10:857–860
Franz S, Gaipl US, Munoz LE, Sheriff A, Beer A, Kalden JR et al (2006) Apoptosis and autoimmunity: when apoptotic cells break their silence. Curr Rheumatol Rep 8:245–247
Coleman ML, Sahai EA, Yeo M, Bosch M, Dewar A, Olson MF (2001) Membrane blebbing during apoptosis results from caspase-mediated activation of ROCK I. Nat Cell Biol 3:339–345
Enari M, Sakahira H, Yokoyama H, Okawa K, Iwamatsu A, Nagata S (1998) A caspase-activated DNase that degrades DNA during apoptosis, and its inhibitor ICAD. Nature 391:43–50
Suzuki J, Denning DP, Imanishi E, Horvitz HR, Nagata S (2013) Xk-related protein 8 and CED-8 promote phosphatidylserine exposure in apoptotic cells. Science 341:403–406
Walczak H (2013) Death receptor-ligand systems in cancer, cell death, and inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 5:a008698
Lavrik IN, Krammer PH (2012) Regulation of CD95/Fas signaling at the DISC. Cell Death Differ 19:36–41
Willis SN, Adams JM (2005) Life in the balance: how BH3-only proteins induce apoptosis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17:617–625
Li H, Zhu H, Xu CJ, Yuan J (1998) Cleavage of BID by caspase 8 mediates the mitochondrial damage in the Fas pathway of apoptosis. Cell 94:491–501
Muller M, Wilder S, Bannasch D, Israeli D, Lehlbach K, Li-Weber M et al (1998) p53 activates the CD95 (APO-1/Fas) gene in response to DNA damage by anticancer drugs. J Exp Med 188:2033–2045
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH, Currie AR (1972) Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer 26:239–257
Kono H, Rock KL (2008) How dying cells alert the immune system to danger. Nat Rev Immunol 8:279–289
Hochreiter-Hufford A, Ravichandran KS (2013) Clearing the dead: apoptotic cell sensing, recognition, engulfment, and digestion. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 5:a008748
Lauber K, Bohn E, Krober SM, Xiao YJ, Blumenthal SG, Lindemann RK et al (2003) Apoptotic cells induce migration of phagocytes via caspase-3-mediated release of a lipid attraction signal. Cell 113:717–730
Truman LA, Ford CA, Pasikowska M, Pound JD, Wilkinson SJ, Dumitriu IE et al (2008) CX3CL1/fractalkine is released from apoptotic lymphocytes to stimulate macrophage chemotaxis. Blood 112:5026–5036
Gude DR, Alvarez SE, Paugh SW, Mitra P, Yu J, Griffiths R et al (2008) Apoptosis induces expression of sphingosine kinase 1 to release sphingosine-1-phosphate as a “come-and-get-me” signal. FASEB J 22:2629–2638
Elliott MR, Chekeni FB, Trampont PC, Lazarowski ER, Kadl A, Walk SF et al (2009) Nucleotides released by apoptotic cells act as a find-me signal to promote phagocytic clearance. Nature 461:282–286
Diaz C, Schroit AJ (1996) Role of translocases in the generation of phosphatidylserine asymmetry. J Membr Biol 151:1–9
Miyanishi M, Tada K, Koike M, Uchiyama Y, Kitamura T, Nagata S (2007) Identification of Tim4 as a phosphatidylserine receptor. Nature 450:435–439
Park D, Tosello-Trampont AC, Elliott MR, Lu M, Haney LB, Ma Z et al (2007) BAI1 is an engulfment receptor for apoptotic cells upstream of the ELMO/Dock180/Rac module. Nature 450:430–434
Park SY, Jung MY, Kim HJ, Lee SJ, Kim SY, Lee BH et al (2008) Rapid cell corpse clearance by stabilin-2, a membrane phosphatidylserine receptor. Cell Death Differ 15:192–201
Kobayashi N, Karisola P, Pena-Cruz V, Dorfman DM, Jinushi M, Umetsu SE et al (2007) TIM-1 and TIM-4 glycoproteins bind phosphatidylserine and mediate uptake of apoptotic cells. Immunity 27:927–940
Nakayama M, Akiba H, Takeda K, Kojima Y, Hashiguchi M, Azuma M et al (2009) Tim-3 mediates phagocytosis of apoptotic cells and cross-presentation. Blood 113:3821–3830
Hanayama R, Tanaka M, Miwa K, Shinohara A, Iwamatsu A, Nagata S (2002) Identification of a factor that links apoptotic cells to phagocytes. Nature 417:182–187
Nakano T, Ishimoto Y, Kishino J, Umeda M, Inoue K, Nagata K et al (1997) Cell adhesion to phosphatidylserine mediated by a product of growth arrest-specific gene 6. J Biol Chem 272:29411–29414
Anderson HA, Maylock CA, Williams JA, Paweletz CP, Shu H, Shacter E (2003) Serum-derived protein S binds to phosphatidylserine and stimulates the phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. Nat Immunol 4:87–91
Savill J, Hogg N, Ren Y, Haslett C (1992) Thrombospondin cooperates with CD36 and the vitronectin receptor in macrophage recognition of neutrophils undergoing apoptosis. J Clin Invest 90:1513–1522
Takizawa F, Tsuji S, Nagasawa S (1996) Enhancement of macrophage phagocytosis upon iC3b deposition on apoptotic cells. FEBS Lett 397:269–272
Chen Y, Park YB, Patel E, Silverman GJ (2009) IgM antibodies to apoptosis-associated determinants recruit C1q and enhance dendritic cell phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. J Immunol 182:6031–6043
Eda S, Yamanaka M, Beppu M (2004) Carbohydrate-mediated phagocytic recognition of early apoptotic cells undergoing transient capping of CD43 glycoprotein. J Biol Chem 279:5967–5974
Chang MK, Bergmark C, Laurila A, Horkko S, Han KH, Friedman P et al (1999) Monoclonal antibodies against oxidized low-density lipoprotein bind to apoptotic cells and inhibit their phagocytosis by elicited macrophages: evidence that oxidation-specific epitopes mediate macrophage recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:6353–6358
Fadok VA, Bratton DL, Konowal A, Freed PW, Westcott JY, Henson PM (1998) Macrophages that have ingested apoptotic cells in vitro inhibit proinflammatory cytokine production through autocrine/paracrine mechanisms involving TGF-beta, PGE2, and PAF. J Clin Invest 101:890–898
Voll RE, Herrmann M, Roth EA, Stach C, Kalden JR, Girkontaite I (1997) Immunosuppressive effects of apoptotic cells. Nature 390:350–351
Huynh ML, Fadok VA, Henson PM (2002) Phosphatidylserine-dependent ingestion of apoptotic cells promotes TGF-beta1 secretion and the resolution of inflammation. J Clin Invest 109:41–50
Stuart LM, Lucas M, Simpson C, Lamb J, Savill J, Lacy-Hulbert A (2002) Inhibitory effects of apoptotic cell ingestion upon endotoxin-driven myeloid dendritic cell maturation. J Immunol 168:1627–1635
Weyd H, Abeler-Dorner L, Linke B, Mahr A, Jahndel V, Pfrang S et al (2013) Annexin A1 on the surface of early apoptotic cells suppresses CD8+ T cell immunity. PLoS One 8:e62449
Ferguson TA, Herndon J, Elzey B, Griffith TS, Schoenberger S, Green DR (2002) Uptake of apoptotic antigen-coupled cells by lymphoid dendritic cells and cross-priming of CD8(+) T cells produce active immune unresponsiveness. J Immunol 168:5589–5595
Getts DR, Turley DM, Smith CE, Harp CT, McCarthy D, Feeney EM et al (2011) Tolerance induced by apoptotic antigen-coupled leukocytes is induced by PD-L1+ and IL-10-producing splenic macrophages and maintained by T regulatory cells. J Immunol 187:2405–2417
Hugues S, Mougneau E, Ferlin W, Jeske D, Hofman P, Homann D et al (2002) Tolerance to islet antigens and prevention from diabetes induced by limited apoptosis of pancreatic beta cells. Immunity 16:169–181
Tomimori Y, Ikawa Y, Oyaizu N (2000) Ultraviolet-irradiated apoptotic lymphocytes produce interleukin-10 by themselves. Immunol Lett 71:49–54
Chen W, Frank ME, Jin W, Wahl SM (2001) TGF-beta released by apoptotic T cells contributes to an immunosuppressive milieu. Immunity 14:715–725
Kim S, Elkon KB, Ma X (2004) Transcriptional suppression of interleukin-12 gene expression following phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. Immunity 21:643–653
Skoberne M, Somersan S, Almodovar W, Truong T, Petrova K, Henson PM et al (2006) The apoptotic-cell receptor CR3, but not alphavbeta5, is a regulator of human dendritic-cell immunostimulatory function. Blood 108:947–955
Wallet MA, Sen P, Flores RR, Wang Y, Yi Z, Huang Y et al (2008) MerTK is required for apoptotic cell-induced T cell tolerance. J Exp Med 205:219–232
AG N, Bensinger SJ, Hong C, Beceiro S, Bradley MN, Zelcer N et al (2009) Apoptotic cells promote their own clearance and immune tolerance through activation of the nuclear receptor LXR. Immunity 31:245–258
Perretti M, Ahluwalia A, Harris JG, Harris HJ, Wheller SK, Flower RJ (1996) Acute inflammatory response in the mouse: exacerbation by immunoneutralization of lipocortin 1. Br J Pharmacol 117:1145–1154
Blume KE, Soeroes S, Waibel M, Keppeler H, Wesselborg S, Herrmann M et al (2009) Cell surface externalization of annexin A1 as a failsafe mechanism preventing inflammatory responses during secondary necrosis. J Immunol 183:8138–8147
Pupjalis D, Goetsch J, Kottas DJ, Gerke V, Rescher U (2011) Annexin A1 released from apoptotic cells acts through formyl peptide receptors to dampen inflammatory monocyte activation via JAK/STAT/SOCS signalling. EMBO Mol Med 3:102–114
Baumann I, Kolowos W, Voll RE, Manger B, Gaipl U, Neuhuber WL et al (2002) Impaired uptake of apoptotic cells into tingible body macrophages in germinal centers of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 46:191–201
Kuhn A, Herrmann M, Kleber S, Beckmann-Welle M, Fehsel K, Martin-Villalba A et al (2006) Accumulation of apoptotic cells in the epidermis of patients with cutaneous lupus erythematosus after ultraviolet irradiation. Arthritis Rheum 54:939–950
Midgley A, McLaren Z, Moots RJ, Edwards SW, Beresford MW (2009) The role of neutrophil apoptosis in juvenile-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 60:2390–2401
Manea ME, Mueller RB, Dejica D, Sheriff A, Schett G, Herrmann M et al (2009) Increased expression of CD154 and FAS in SLE patients’ lymphocytes. Rheumatol Int 30:181–185
Sahebari M, Rezaieyazdi Z, Nakhjavani MJ, Hatef M, Mahmoudi M, Akhlaghi S (2012) Correlation between serum concentrations of soluble Fas (CD95/Apo-1) and IL-18 in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Int 32:601–606
Toberer F, Sykora J, Goettel D, Hartschuh W, Werchau S, Enk A et al (2013) Apoptotic signal molecules in skin biopsies of cutaneous lupus erythematosus: analysis using tissue microarray. Exp Dermatol 22:656–659
Viard-Leveugle I, Bullani RR, Meda P, Micheau O, Limat A, Saurat JH et al (2003) Intracellular localization of keratinocyte Fas ligand explains lack of cytolytic activity under physiological conditions. J Biol Chem 278:16183–16188
Bennett M, Macdonald K, Chan SW, Luzio JP, Simari R, Weissberg P (1998) Cell surface trafficking of Fas: a rapid mechanism of p53-mediated apoptosis. Science 5387:290–293
Daniels F Jr, Brophy D, Lobitz WC Jr (1961) Histochemical responses of human skin following ultraviolet irradiation. J Invest Dermatol 37:351–357
Matsunaga T, Hieda K, Nikaido O (1991) Wavelength dependent formation of thymine dimers and (6–4) photoproducts in DNA by monochromatic ultraviolet light ranging from 150 to 365 nm. Photochem Photobiol 54:403–410
Bates S, Vousden KH (1999) Mechanisms of p53-mediated apoptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci 55:28–37
Rehemtulla A, Hamilton CA, Chinnaiyan AM, Dixit VM (1997) Ultraviolet radiation-induced apoptosis is mediated by activation of CD-95 (Fas/APO-1). J Biol Chem 272:25783–25786
Assefa Z, Garmyn M, Vantieghem A, Declercq W, Vandenabeele P, Vandenheede JR et al (2003) Ultraviolet B radiation-induced apoptosis in human keratinocytes: cytosolic activation of procaspase-8 and the role of Bcl-2. FEBS Lett 540:125–132
Assefa Z, Vantieghem A, Garmyn M, Declercq W, Vandenabeele P, Vandenheede JR et al (2000) p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase regulates a novel, caspase-independent pathway for the mitochondrial cytochrome c release in ultraviolet B radiation-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 275:21416–21421
Herrmann M, Voll RE, Zoller OM, Hagenhofer M, Ponner BB, Kalden JR (1998) Impaired phagocytosis of apoptotic cell material by monocyte-derived macrophages from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 41:1241–1250
Hanayama R, Tanaka M, Miyasaka K, Aozasa K, Koike M, Uchiyama Y et al (2004) Autoimmune disease and impaired uptake of apoptotic cells in MFG-E8-deficient mice. Science 304:1147–1150
Pickering MC, Botto M, Taylor PR, Lachmann PJ, Walport MJ (2000) Systemic lupus erythematosus, complement deficiency, and apoptosis. Adv Immunol 76:227–324
Casciola-Rosen LA, Anhalt G, Rosen A (1994) Autoantigens targeted in systemic lupus erythematosus are clustered in two populations of surface structures on apoptotic keratinocytes. J Exp Med 179:1317–1330
Ronnblom L, Eloranta ML, Alm GV (2006) The type I interferon system in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 54:408–420
Lauber K, Keppeler H, Munoz LE, Koppe U, Schroder K, Yamaguchi H et al (2013) Milk fat globule-EGF factor 8 mediates the enhancement of apoptotic cell clearance by glucocorticoids. Cell Death Differ 20:1230–1240
Abeler-Dörner L, Rieger CC, Berger B, Weyd H, Gräf D, Pfrang S et al (2013) Interferon-α abrogates the suppressive effect of apoptotic cells on dendritic cells in an in vitro model of systemic lupus erythematosus pathogenesis. J Rheumatol 40:1683–1696
George PM, Badiger R, Alazawi W, Foster GR, Mitchell JA (2012) Pharmacology and therapeutic potential of interferons. Pharmacol Ther 135:44–53
Arur S, Uche UE, Rezaul K, Fong M, Scranton V, Cowan AE et al (2003) Annexin I is an endogenous ligand that mediates apoptotic cell engulfment. Dev Cell 4:587–598
Scannell M, Flanagan MB, deStefani A, Wynne KJ, Cagney G, Godson C et al (2007) Annexin-1 and peptide derivatives are released by apoptotic cells and stimulate phagocytosis of apoptotic neutrophils by macrophages. J Immunol 178:4595–4605
Szodoray P, Tarr T, Tumpek J, Kappelmayer J, Lakos G, Poor G et al (2009) Identification of rare anti-phospholipid/protein co-factor autoantibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmunity 42:497–506
Kretz CC, Norpo M, Abeler-Dorner L, Linke B, Haust M, Edler L et al (2010) Anti-annexin 1 antibodies: a new diagnostic marker in the serum of patients with discoid lupus erythematosus. Exp Dermatol 19:919–921
Lindenmann J (2007) Interferon and before. J Interferon Cytokine Res 27:2–5
Agmon-Levin N, Blank M, Paz Z, Shoenfeld Y (2009) Molecular mimicry in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 18:1181–1185
Elkon KB, Wiedeman A (2012) Type I IFN system in the development and manifestations of SLE. Curr Opin Rheumatol 24:499–505
Hagberg N, Berggren O, Leonard D, Weber G, Bryceson YT, Alm GV et al (2011) IFN-alpha production by plasmacytoid dendritic cells stimulated with RNA-containing immune complexes is promoted by NK cells via MIP-1beta and LFA-1. J Immunol 186:5085–5094
Gehrke N, Mertens C, Zillinger T, Wenzel J, Bald T, Zahn S et al (2013) Oxidative damage of DNA confers resistance to cytosolic nuclease TREX1 degradation and potentiates STING-dependent immune sensing. Immunity 39:482–495
Ronnblom LE, Alm GV, Oberg KE (1990) Possible induction of systemic lupus erythematosus by interferon-alpha treatment in a patient with a malignant carcinoid tumour. J Intern Med 227:207–210
Ronnblom L, Alm GV, Eloranta ML (2011) The type I interferon system in the development of lupus. Semin Immunol 23:113–121
Dall’era MC, Cardarelli PM, Preston BT, Witte A, Davis JC Jr (2005) Type I interferon correlates with serological and clinical manifestations of SLE. Ann Rheum Dis 64:1692–1697
Ronnblom L, Alm GV (2001) An etiopathogenic role for the type I IFN system in SLE. Trends Immunol 22:427–431
Baechler EC, Batliwalla FM, Karypis G, Gaffney PM, Ortmann WA, Espe KJ et al (2003) Interferon-inducible gene expression signature in peripheral blood cells of patients with severe lupus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:2610–2615
Bennett L, Palucka AK, Arce E, Cantrell V, Borvak J, Banchereau J et al (2003) Interferon and granulopoiesis signatures in systemic lupus erythematosus blood. J Exp Med 197:711–723
Fah J, Pavlovic J, Burg G (1995) Expression of MxA protein in inflammatory dermatoses. J Histochem Cytochem 43:47–52
Freutel S, Gaffal E, Zahn S, Bieber T, Tuting T, Wenzel J (2011) Enhanced CCR5+/CCR3+ T helper cell ratio in patients with active cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Lupus 20:1300–1304
Wenzel J, Tuting T (2008) An IFN-associated cytotoxic cellular immune response against viral, self-, or tumor antigens is a common pathogenetic feature in “interface dermatitis”. J Invest Dermatol 128:2392–2402
Guiducci C, Tripodo C, Gong M, Sangaletti S, Colombo MP, Coffman RL et al (2010) Autoimmune skin inflammation is dependent on plasmacytoid dendritic cell activation by nucleic acids via TLR7 and TLR9. J Exp Med 207:2931–2942
Arrue I, Saiz A, Ortiz-Romero PL, Rodriguez-Peralto JL (2007) Lupus-like reaction to interferon at the injection site: report of five cases. J Cutan Pathol 34(Suppl 1):18–21
Wenzel J, Zahn S, Mikus S, Wiechert A, Bieber T, Tuting T (2007) The expression pattern of interferon-inducible proteins reflects the characteristic histological distribution of infiltrating immune cells in different cutaneous lupus erythematosus subsets. Br J Dermatol 157:752–757
Tomasini D, Mentzel T, Hantschke M, Cerri A, Paredes B, Rutten A et al (2010) Plasmacytoid dendritic cells: an overview of their presence and distribution in different inflammatory skin diseases, with special emphasis on Jessner’s lymphocytic infiltrate of the skin and cutaneous lupus erythematosus. J Cutan Pathol 37:1132–1139
Wenzel J, Tuting T (2007) Identification of type I interferon-associated inflammation in the pathogenesis of cutaneous lupus erythematosus opens up options for novel therapeutic approaches. Exp Dermatol 16:454–463
Zahn S, Rehkamper C, Kummerer BM, Ferring-Schmidt S, Bieber T, Tuting T et al (2011) Evidence for a pathophysiological role of keratinocyte-derived type III interferon (IFNlambda) in cutaneous lupus erythematosus. J Invest Dermatol 131:133–140
Bose A, Baral R (2007) IFNalpha2b stimulated release of IFNgamma differentially regulates T cell and NK cell mediated tumor cell cytotoxicity. Immunol Lett 108:68–77
Zella D, Barabitskaja O, Casareto L, Romerio F, Secchiero P, Reitz MS Jr et al (1999) Recombinant IFN-alpha (2b) increases the expression of apoptosis receptor CD95 and chemokine receptors CCR1 and CCR3 in monocytoid cells. J Immunol 163:3169–3175
Zahn S, Rehkamper C, Ferring-Schmitt S, Bieber T, Tuting T, Wenzel J (2011) Interferon-alpha stimulates TRAIL expression in human keratinocytes and peripheral blood mononuclear cells: implications for the pathogenesis of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Br J Dermatol 165:1118–1123
Zampieri S, Alaibac M, Iaccarino L, Rondinone R, Ghirardello A, Sarzi-Puttini P et al (2006) Tumour necrosis factor alpha is expressed in refractory skin lesions from patients with subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 65:545–548
Norman R, Greenberg RG, Jackson JM (2006) Case reports of etanercept in inflammatory dermatoses. J Am Acad Dermatol 54:S139–S142
Vedove CD, Del Giglio M, Schena D, Girolomoni G (2009) Drug-induced lupus erythematosus. Arch Dermatol Res 301:99–105
Fiorentino DF (2007) The Yin and Yang of TNF-{alpha} inhibition. Arch Dermatol 143:233–236
Aringer M, Burkhardt H, Burmester GR, Fischer-Betz R, Fleck M, Graninger W et al (2012) Current state of evidence on ‘off-label’ therapeutic options for systemic lupus erythematosus, including biological immunosuppressive agents, in Germany, Austria and Switzerland—a consensus report. Lupus 21:386–401
Kuhn A, Ochsendorf F, Bonsmann G (2010) Treatment of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Lupus 19:1125–1136
Ochsendorf FR (2010) Use of antimalarials in dermatology. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 8:829–844, quiz 45
Kuhn A, Ruland V, Bonsmann G (2011) Cutaneous lupus erythematosus: update of therapeutic options. Part I. J Am Acad Dermatol 65:e179–e193
Patsinakidis N, Wenzel J, Landmann A, Koch R, Gerss J, Luger TA et al (2012) Suppression of UV-induced damage by a liposomal sunscreen: a prospective, open-label study in patients with cutaneous lupus erythematosus and healthy controls. Exp Dermatol 21:958–961
Baker VS, Imade GE, Molta NB, Tawde P, Pam SD, Obadofin MO et al (2008) Cytokine-associated neutrophil extracellular traps and antinuclear antibodies in Plasmodium falciparum infected children under six years of age. Malar J 7:41
Sharma S, DeOliveira RB, Kalantari P, Parroche P, Goutagny N, Jiang Z et al (2011) Innate immune recognition of an AT-rich stem-loop DNA motif in the Plasmodium falciparum genome. Immunity 35:194–207
Kuznik A, Bencina M, Svajger U, Jeras M, Rozman B, Jerala R (2011) Mechanism of endosomal TLR inhibition by antimalarial drugs and imidazoquinolines. J Immunol 186:4794–4804
Chang AY, Piette EW, Foering KP, Tenhave TR, Okawa J, Werth VP (2011) Response to antimalarial agents in cutaneous lupus erythematosus: a prospective analysis. Arch Dermatol 147:1261–1267
Baima B, Sticherling M (2001) Apoptosis in different cutaneous manifestations of lupus erythematosus. Br J Dermatol 144:958–966
Petri M, Wallace DJ, Spindler A, Chindalore V, Kalunian K, Mysler E et al (2013) Sifalimumab, a human anti-interferon-alpha monoclonal antibody, in systemic lupus erythematosus: a phase I randomized, controlled, dose-escalation study. Arthritis Rheum 65:1011–1021
Wang B, Higgs BW, Chang L, Vainshtein I, Liu Z, Streicher K et al (2013) Pharmacogenomics and translational simulations to bridge indications for an anti-interferon-alpha receptor antibody. Clin Pharmacol Ther 93:483–492
Meyer O (2012) Interferon-alpha as a treatment target in systemic lupus erythematosus. Jt Bone Spine 79:113–116
Kubo S, Yamaoka K, Kondo M, Yamagata K, Zhao J, Iwata S et al (2013) The JAK inhibitor, tofacitinib, reduces the T cell stimulatory capacity of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Ann Rheum Dis. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203756
Wolska H, Blaszczyk M, Jablonska S (1989) Phototests in patients with various forms of lupus erythematosus. Int J Dermatol 28:98–103
van Weelden H, Velthuis PJ, Baart de la Faille H (1989) Light-induced skin lesions in lupus erythematosus: photobiological studies. Arch Dermatol 281:470–474
Beutner EH, Blaszczyk M, Jablonska S, Chorzelski TP, Vijay K, Wolska H (1991) Studies on criteria of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology for the classification of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Int J Dermatol 30:411–417
Kind P, Lehmann P, Plewig G (1993) Phototesting in lupus erythematosus. J Invest Dermatol 100:53S–57S
Nived O, Johansen PB, Sturfelt G (1993) Standardized ultraviolet-A exposure provoces skin reaction in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2:247–250
Bensaid P, Vaillant L, Esteve E, Machet MC, Machet L, Lorette G (1995) Photobiological study of lupus erythematosus. Ann Dermatol Venereol 122:84–89
Walchner M, Messer G, Kind P (1997) Phototesting and photoprotection in LE. Lupus 6:167–174
Hasan T, Nyberg F, Stephansson E, Puska P, Hakkinen M, Sarna S et al (1997) Photosensitivity in lupus erythematosus, UV photoprovocation results compared with history of photosensitivity and clinical findings. Br J Dermatol 136:699–705
Leenutaphong V, Boonchai W (1999) Phototesting in oriental patients with lupus erythematosus. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 15:7–12
Kuhn A, Sonntag M, Richter-Hintz D, Oslislo C, Megahed M, Ruzicka T et al (2001) Phototesting in lupus erythematosus tumidus—review of 60 patients. Photochem Photobiol 73:532–536
Sanders CJ, Van Weelden H, Kazzaz GA, Sigurdsson V, Toonstra J, Bruijnzeel-Koomen CA (2003) Photosensitivity in patients with lupus erythematosus: a clinical and photobiological study of 100 patients using a prolonged phototest protocol. Br J Dermatol 149:131–137
Choonhakarn C, Poonsriaram A, Chaivoramukul J (2004) Lupus erythematosus tumidus. Int J Dermatol 43:815–818
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuhn, A., Wenzel, J. & Weyd, H. Photosensitivity, Apoptosis, and Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Lupus Erythematosus: a Critical Review. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 47, 148–162 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-013-8403-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-013-8403-x