Abstract
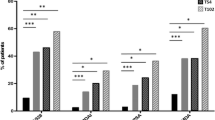
The aim of the study was to evaluate the influence of metabolic syndrome (MetS) on achieving minimal disease activity (MDA) in psoriatic arthritis (PsA) patients treated with anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α with a follow-up period of 24 months. A cohort of PsA patients was assessed at the University Federico II of Naples and at University of Padova. For the aim of the present study, patients’ data were collected at baseline (T0), at 12 months (T1) and at 24 months (T2). Assessment of metabolic and disease activity parameters was performed at each visit. The NCEP-ACT III criteria were used to identify subjects with MetS and the MDA criteria to evaluate the disease activity. On the basis of the exclusion and inclusion criteria, 330 subjects were included in the study; 134 patients (40.7 %) were classified as not having MetS and 196 (59.3 %) as having MetS. An inverse association was found between presence of metabolic syndrome and the probability of achieving MDA. Univariate analysis indicated that patients with metabolic syndrome were less likely to achieve MDA than patients without metabolic syndrome (OR 0.45, p < 0.001). This inverse association remained statistically significant in the multivariate regression model (OR 0.56, p < 0.001). Metabolic syndrome is associated with a lower probability of achieving MDA in PsA patients in therapy with anti-TNF-α.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moll JM, Wright V. Psoriatic arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1973;3:55–78.
Raychaudhuri SK, Maverakis E, Raychaudhuri SP. Diagnosis and classification of psoriasis. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13:490–5.
Soscia E, Sirignano C, Catalano O, Atteno M, Costa L, Caso F, Peluso R, Bruner V, Aquino MM, Del Puente A, Salvatore M, Scarpa R. New developments in magnetic resonance imaging of the nail unit. J Rheumatol Suppl. 2012;89:49–53.
Taylor W, Gladman D, Helliwell P, Marchesoni A, Mease P, Mielants H. Classification criteria for psoriatic arthritis: development of new criteria from a large international study. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:2665–73.
Tillett W, Costa L, Jadon D, Wallis D, Cavill C, McHugh J, Korendowych E, McHugh N. The classification for psoriatic arthritis (CASPAR) criteria—a retrospective feasibility, sensitivity, and specificity study. J Rheumatol. 2012;39:154–6.
Chimenti MS, Ballanti E, Perricone C, Cipriani P, Giacomelli R, Perricone R. Immunomodulation in psoriatic arthritis: focus on cellular and molecular pathways. Autoimmun Rev. 2013;12:599–606.
Fiocco U, Accordi B, Martini V, Oliviero F, Facco M, Cabrelle A, Piva L, Molena B, Caso F, Costa L, Scanu A, Pagnin E, Atteno M, Scarpa R, Basso G, Semenzato G, Punzi L, Doria A, Dayer JM. JAK/STAT/PKCδ molecular pathways in synovial fluid T lymphocytes reflect the in vivo T helper-17 expansion in psoriatic arthritis. Immunol Res. 2014;58:61–9.
Suzuki E, Mellins ED, Gershwin ME, Nestle FO, Adamopoulos IE. The IL-23/IL-17 axis in psoriatic arthritis. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13:496–502.
Ballanti E, Perricone C, di Muzio G, Kroegler B, Chimenti MS, Graceffa D, Perricone R. Role of the complement system in rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis: relationship with anti-TNF inhibitors. Autoimmun Rev. 2011;10:617–23.
Scarpa R, Costa L, Atteno M, Del Puente A, Caso F, Moll JM. Psoriatic arthritis: advances in pharmacotherapy based on molecular target. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2013;14:2311–3.
Novelli L, Chimenti MS, Chiricozzi A, Perricone R. The new era for the treatment of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: perspectives and validated strategies. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13:64–9.
Fiorino G, Girolomoni G, Lapadula G, Orlando A, Danese S, Olivieri I. SIR, SIDeMaST, and IG-IBD. The use of biosimilars in immune-mediated disease: a joint Italian society of rheumatology (SIR), Italian society of dermatology (SIDeMaST), and Italian group of inflammatory bowel disease (IG-IBD) position paper. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13:751–5.
Fiocco U, Sfriso P, Oliviero F, Lunardi F, Calabrese F, Scagliori E, Cozzi L, Di Maggio A, Nardacchione R, Molena B, Felicetti M, Gazzola K, Stramare R, Rubaltelli L, Accordi B, Costa L, Roux-Lombard P, Punzi L, Dayer JM. Blockade of intra-articular TNF in peripheral spondyloarthritis: its relevance to clinical scores, quantitative imaging and synovial fluid and synovial tissue biomarkers. Jt Bone Spine. 2013;80:165–70.
Scarpa R, Atteno M, Lubrano E, Provenzano G, D’Angelo S, Spadaro A, Costa L, Olivieri I. The effectiveness and safety of TNF-alpha blockers in the treatment of early psoriatic arthritis: an Italian multicentre longitudinal observational pilot study. Clin Rheumatol. 2011;30:1063–7.
Chimenti MS, Graceffa D, Perricone R. Anti-TNFα discontinuation in rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis: is it possible after disease remission? Autoimmun Rev. 2011;10:636–40.
Atteno M, Costa L, Matarese A, Caso F, Del Puente A, Cantarini L, Bocchino ML, Sanduzzi A, Scarpa R. The use of TNF-α blockers in psoriatic arthritis patients with latent tuberculosis infection. Clin Rheumatol. 2014;33:543–7.
Costa L, Caso F, Atteno M, Giannitti C, Spadaro A, Ramonda R, Vezzù M, Del Puente A, Morisco F, Fiocco U, Galeazzi M, Punzi L, Scarpa R. Long-term safety of anti-TNF-α in PsA patients with concomitant HCV infection: a retrospective observational multicenter study on 15 patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2014;33:273–6.
Sanduzzi A, Bocchino M, Atteno M, Costa L, Ponticiello A, Matarese A, Spanò A, Bruner V, Peluso R, Aquino MM, Del Puente A, Scarpa R. Screening and monitoring of latent tubercular infection in patients taking tumor necrosis factor-α blockers for psoriatic arthritis. J Rheumatol Suppl. 2012;89:82–5.
Fiorino G, Danese S, Pariente B, Allez M. Paradoxical immune-mediated inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease patients receiving anti-TNF-α agents. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13:15–9.
Piga M, Chessa E, Ibba V, Mura V, Floris A, Cauli A, Mathieu A. Biologics-induced autoimmune renal disorders in chronic inflammatory rheumatic diseases: systematic literature review and analysis of a monocentric cohort. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13:873–9.
Selmi C. Diagnosis and classification of autoimmune uveitis. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13:591–4.
Scarpa R, Ayala F, Caporaso N, Olivieri I. Psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, or psoriatic disease? J Rheumatol. 2006;33:210–2.
Ritchlin CT. From skin to bone: translational perspectives on psoriatic disease. J Rheumatol. 2008;35:1434–7.
Boehncke WH, Boehncke S. Cardiovascular mortality in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: epidemiology, pathomechanisms, therapeutic implications, and perspectives. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2012;14:343–8.
Ramonda R, Lo Nigro A, Modesti V, Nalotto L, Musacchio E, Iaccarino L, Punzi L, Doria A. Atherosclerosis in psoriatic arthritis. Autoimmun Rev. 2011;10:773–8.
Sarzi-Puttini P, Atzeni F, Gerli R, Bartoloni E, Doria A, Barskova T, Matucci-Cerinic M, Sitia S, Tomasoni L, Turiel M. Cardiac involvement in systemic rheumatic diseases: an update. Autoimmun Rev. 2010;9:849–52.
Ramonda R, Puato M, Punzi L, Rattazzi M, Zanon M, Balbi G, Ortolan A, Frallonardo P, Faggin E, Plebani M, Zaninotto M, Lorenzin M, Pauletto P, Doria A. Atherosclerosis progression in psoriatic arthritis patients despite the treatment with tumor necrosis factor-alpha blockers: a two-year prospective observational study. Jt Bone Spine. 2014;. doi:10.1016/j.jbspin.2014.02.005.
Costa L, Caso F, D’Elia L, Atteno M, Peluso R, Del Puente A, Strazzullo P, Scarpa R. Psoriatic arthritis is associated with increased arterial stiffness in the absence of known cardiovascular risk factors: a case control study. Clin Rheumatol. 2012;31:711–5.
Mok CC, Ko GT, Ho LY, Yu KL, Chan PT, To CH. Prevalence of atherosclerotic risk factors and the metabolic syndrome in patients with chronic inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011;63:195–202.
Raychaudhuri SK, Chatterjee S, Nguyen C, Kaur M, Jialal I, Raychaudhuri SP. Increased prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in patients with psoriatic arthritis. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2010;8:331–4.
Pereira RM, de Carvalho JF, Bonfá E. Metabolic syndrome in rheumatological diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 2009;8:415–9.
Raychaudhuri SP. Comorbidities of psoriatic arthritis—metabolic syndrome and prevention: a report from the GRAPPA 2010 annual meeting. J Rheumatol. 2012;39:437–40.
Eder L, Jayakar J, Pollock R, Pellett F, Thavaneswaran A, Chandran V, Rosen CF, Gladman DD. Serum adipokines in patients with psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis alone and their correlation with disease activity. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202325.
Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ. The metabolic syndrome. Lancet. 2005;365:1415–28.
Tam LS, Tomlinson B, Chu TT, Li M, Leung YY, Kwok LW, et al. Cardiovascular risk profile of patients with psoriatic arthritis compared to controls—The role of inflammation. Rheumatology. 2008;47:718–23.
Jones SM, Harris CP, Lloyd J, Stirling CA, Reckless JP, McHugh NJ. Lipoproteins and their subfractions in psoriatic arthritis: identification of an atherogenic profile with active joint disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000;59:904–9.
Costa L, Caso F, Atteno M, Del Puente A, Darda MA, Caso P, Ortolan A, Fiocco U, Ramonda R, Punzi L, Scarpa R. Impact of 24-month treatment with etanercept, adalimumab, or methotrexate on metabolic syndrome components in a cohort of 210 psoriatic arthritis patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2014;33:833–9.
Suryaprasad AG, Prindiville T. The biology of TNF blockade. Autoimmun Rev. 2003;2:346–57.
Hotamisligil GS. Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature. 2006;444:860–7.
Executive Summary of The Third Report of The. National cholesterol education program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). Expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults. JAMA. 2001;285:2486–97.
Coates LC, Fransen J, Helliwell PS. Defining minimal disease activity in psoriatic arthritis: a proposed objective target for treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:48–53.
Coates LC, Helliwell PS. Validation of minimal disease activity criteria for psoriatic arthritis using interventional trial data. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2010;62:965–9.
Haroon M, Gallagher P, Heffernan E, FitzGerald O. High prevalence of metabolic syndrome and of insulin resistance in psoriatic arthritis is associated with the severity of underlying disease. J Rheumatol. 2014;41:1357–65.
Eder L, Thavaneswaran A, Chandran V, Cook RJ, Gladman DD. Obesity is associated with a lower probability of achieving sustained minimal disease activity state among patients with psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204448.
di Minno MN, Peluso R, Iervolino S, Lupoli R, Russolillo A, Scarpa R, di Minno G. Obesity and the prediction of minimal disease activity: a prospective study in psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2013;65:141–7.
Choi KM, Ryu OH, Lee KW, et al. Serum adiponectin, interleukin-10 levels and inflammatory markers in the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007;75:235–40.
Trayhurn P, Wood IS. Adipokines: inflammation and the pleiotropic role of white adipose tissue. Br J Nutr. 2004;92:347–55.
Sethi JK, Hotamisligil GS. The role of TNF alpha in adipocyte metabolism. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 1999;10:19–29.
Gremese E, Ferraccioli G. The metabolic syndrome: the crossroads between rheumatoid arthritis and cardiovascular risk. Autoimmun Rev. 2011;10:582–9.
Fonseca JE, Santos MJ, Canhão H, Choy E. Interleukin-6 as a key player in systemic inflammation and joint destruction. Autoimmun Rev. 2009;8:538–42.
Scrivo R, Vasile M, Bartosiewicz I, Valesini G. Inflammation as “common soil” of the multifactorial diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 2011;10:369–74.
Mease PJ. Tumour necrosis factor (TNF) in psoriatic arthritis: pathophysiology and treatment with TNF inhibitors. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002;61:298–304.
Abou-Raya A, Abou-Raya S. Inflammation: a pivotal link between autoimmune diseases and atherosclerosis. Autoimmun Rev. 2006;5:331–7.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Luisa Costa and Francesco Caso have contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costa, L., Caso, F., Ramonda, R. et al. Metabolic syndrome and its relationship with the achievement of minimal disease activity state in psoriatic arthritis patients: an observational study. Immunol Res 61, 147–153 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-014-8595-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-014-8595-z