Abstract
-
▲ Febuxostat is an orally administered, non-purine, selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase approved for the management of chronic hyperuricaemia in patients with gout.
-
▲ In a randomized, double-blind, dose-ranging study in patients with gout and hyperuricaemia, significantly more recipients of febuxostat 40–120 mg/day than placebo had serum urate levels of <6.0 mg/dL after 4 weeks of treatment.
-
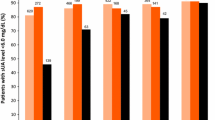
▲ Serum urate levels were reduced below 6.0 mg/dL at the last three monthly observations in a significantly greater proportion of patients with gout and hyperuricaemia receiving febuxostat 80 or 120 mg once daily than in those receiving allopurinol 300 mg once daily in a 52-week, randomized, double-blind trial (FACT).
-
▲ Similarly, febuxostat 80, 120 or 240 mg once daily showed significantly greater urate-lowering efficacy than allopurinol 100 or 300 mg once daily in a 28-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (APEX) in patients with gout and hyperuricaemia.
-
▲ Long-term treatment with febuxostat for up to 4 years or more reduced the incidence of gout flares to (or close to) zero.
-
▲ Febuxostat was generally well tolerated in clinical trials, including extension studies lasting ≥4 years, with most treatment-related adverse events being mild to moderate in severity.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The use of trade names is for product identification purposes only and does not imply endorsement.
References
Arromdee E, Michet CJ, Crowson CS, et al. Epidemiology of gout: is the incidence rising? J Rheumatol 2002; 29(11): 2403–6
Luk AJ, Simkin PA. Epidemiology of hyperuricemia and gout. Am J Manag Care 2005; 11 (15 Suppl.): S435–42
Adams PF, Hendershot GE, Marano MA. Current estimates from the National Health Interview Survey, 1996. National Center for Health Statistics. Vital Health Stat 1999; 10 (200) [online]. Available from URL: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/series/sr_10/srl0_200.pdf [Accessed 2006 Apr 18]
Wallace KL, Riedel AA, Joseph-Ridge N, et al. Increasing prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia over 10 years among older adults in a managed care population. J Rheumatol 2004; 31(8): 1582–7
Choi HK, Mount DB, Reginato AM. Pathogenesis of gout. Ann Intern Med 2005 Oct 4; 143(7): 499–516
Terkeltaub RA. Gout. N Engl J Med 2003 Oct 23; 349(17): 1647–55
Hoskison KT, Wortmann RL. Management of gout in older adults: barriers to optimal control. Drugs Aging 2007; 24(1): 21–36
Schlesinger N. Management of acute and chronic gouty arthritis: present state-of-the-art. Drugs 2004; 64(21): 2399–416
Wortmann RL, Schumacher Jr HR. Monosodium urate deposition arthropathy part II: treatment and long-term management of patients with gout. Adv Studies Med 2005; 5(4): 183–94
Okamoto K, Eger BT, Nishino T, et al. An extremely potent inhibitor of xanthine oxidoreductase. Crystal structure of the enzyme-inhibitor complex and mechanism of inhibition. J Biol Chem 2003 Jan 17; 278(3): 1848–55
Schumacher Jr HR. Febuxostat: a non-purine, selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase for the management of hyperuricaemia in patients with gout. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2005 Jul; 14(7): 893–903
Perez-Ruiz F, Alonso-Ruiz A, Calabozo M, et al. Efficacy of allopurinol and benzbromarone for the control of hyperuricaemia: a pathogenic approach to the treatment of primary gout. Ann Rheum Dis 1998 Sep; 57(9): 545–9
Ipsen. Adenuric® (febuxostat) receives marketing authorisation in the European Union [media release]. 2008 May 5
Yamamoto T, Moriwaki Y, Fujimura Y, et al. Effect of TEI-6720, a xanthine oxidase inhibitor, on the nucleoside transport in the lung cancer cell line A 549. Pharmacology 2000 Jan; 60(1): 34–40
Takano Y, Hase-Aoki K, Horiuchi H, et al. Selectivity of febuxostat, a novel non-purine inhibitor of xanthine oxidase/xanthine dehydrogenase. Life Sci 2005 Mar 4; 76(16): 1835–47
Osada Y, Tsuchimoto M, Fukushima H, et al. Hypouricemic effect of the novel xanthine oxidase inhibitor, TEI-6720, in rodents. Eur J Pharmacol 1993 Sep 14; 241(2–3): 183–8
Komoriya K, Osada Y, Hasegawa M, et al. Hypouricemic effect of allopurinol and the novel xanthine oxidase inhibitor TEI-6720 in chimpanzees. Eur J Pharmacol 1993 Dec 21; 250(3): 455–60
Becker MA, Kisicki J, Khosravan R, et al. Febuxostat (TMX-67), a novel, non-purine, selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase, is safe and decreases serum urate in healthy volunteers. Nucleos Nucleot Nucleic Acids 2004 Oct; 23(8–9): 1111–6
Khosravan R, Kukulka MJ, Wu JT, et al. The effect of age and gender on pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety of febuxostat, a novel nonpurine selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase. J Clin Pharmacol. Epub 2008 Jul 17
Mayer MD, Khosravan R, Vernillet L, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of febuxostat, a new non-purine selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase in subjects with renal impairment. Am J Ther 2005; 12(1): 22–34
Khosravan R, Grabowski BA, Mayer MD, et al. The effect of mild and moderate hepatic impairment on pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety of febuxostat, a novel nonpurine selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase. J Clin Pharmacol 2006 Jan; 46(1): 88–102
Becker MA, Schumacher Jr HR, Wortmann RL, et al. Febuxostat, a novel nonpurine selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase: a twenty-eight-day, multicenter, phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-response clinical trial examining safety and efficacy in patients with gout. Arthritis Rheum 2005 Mar; 52(3): 916–23
Khosravan R, Wu J-T, Lademacher C, et al. Effect of febuxostat on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of warfarin [abstract no. 71]. J Clin Pharmacol 2005 Sep; 45(9): 1084
Grabowski BA, Khosravan R, Wu J-T, et al. Effect of hydrochlorothiazide on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of febuxostat [abstract no. 190]. Arthritis Rheum 2005 Sep; 52 (9 Suppl.): S103–4. Plus poster presented at the 69th Annual Scientific Meeting of the American College of Rheumatology and the 40th Annual Meeting of the Association of Rheumatology Health Professionals; 2005 Nov 12–17; San Diego (CA)
Khosravan R, Wu J-T, Joseph-Ridge N, et al. Pharmacokinetic interactions of concomitant administration of febuxostat and NSAIDs. J Clin Pharmacol 2006 Aug; 46(8): 855–66
Khosravan R, Mayer MD, Wu J-T, et al. Effect of concomitant administration of febuxostat and colchicine on pharmacokinetics of febuxostat and colchicine at steady state [abstract no. 188]. Arthritis Rheum 2005 Sep; 52 (9 Suppl.): S102–3. Plus poster presented at the 69th Annual Scientific Meeting of the American College of Rheumatology and the 40th Annual Meeting of the Association of Rheumatology Health Professionals; 2005 Nov 12–17; San Diego (CA)
Khosravan R, Erdman K, Vernillet L, et al. Effect of febuxostat on pharmacokinetics of desipramine, a CYP2D6 substrate, in healthy subjects [abstract no. PI-137]. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2005 Feb; 77(2): P43
Khosravan R, Grabowski B, Wu JT, et al. Effect of food or antacid on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of febuxostat in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2007; 65(3): 355–63
Mukoyoshi M, Nishimura S, Hoshide S, et al. In vitro drug-drug interaction studies with febuxostat, a novel non-purine selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase: plasma protein binding, identification of metabolic enzymes and cytochrome P450 inhibition. Xenobiotica 2008 May; 38(5): 496–510
European Medicines Agency. Adenuric (febuxostat): summary of product characteristics [online]. Available from URL: http://www.emea.europa.eu/humandocs/PDFs/EPAR/adenuric/H-777-PI-en.pdf [Accessed 2008 Aug 1]
Bardin T. Current management of gout in patients unresponsive or allergic to allopurinol. Joint Bone Spine 2004; 71(6): 481–5
Becker MA, Schumacher Jr HR, Wortmann RL, et al. Febuxostat compared with allopurinol in patients with hyperuricaemia and gout. N Engl J Med 2005 Dec 8; 353(23): 2450–61
Schumacher HR, Becker MA, Wortmann RL, et al. Febuxostat vs allopurinol and placebo in subjects with hyperuricaemia and gout: the 28-week APEX study [abstract no. 1837]. Arthritis Rheum 2005 Sep; 52 (9 Suppl.): S680
Becker MA, Schumacher HR, Wortmann RL, et al. The long-term clinical benefits of febuxostat vs allopurinol in subjects with gout: interim analysis of the EXCEL trial, an ongoing phase 3, open-label extension study [abstract no. FRI0483]. Ann Rheum Dis 2006 Jul; 65 Suppl. II: 431
Becker MA, Schumacher Jr HR, MacDonald PA, et al. Uratelowering therapy (febuxostat or allopurinol) in subjects with gout interim results from the Febuxostat Comparative Extension Long-term Study (EXCEL) [abstract no. 757]. Arthritis Rheum 2007 Sep; 56 (9 Suppl.): S322
Wortmann RL, Becker MA, Schumacher Jr HR, et al. Effect of febuxostat or allopurinol on the clinical manifestations of gout: reduction in gout flares and tophus size over time in the EXCEL trial [abstract no. 1592]. Arthritis Rheum 2006 Sep; 54 (9 Suppl.): S642
Schumacher HR, Wortmann R, Becker M, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of febuxostat, a novel non-purine selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase, in subjects with hyperuricemia and gout [abstract no. SAT0282]. Ann Rheum Dis 2005 Jul; 64 Suppl. 3: 498
Becker MA, Schumacher R, Wortmann R, et al. Febuxostat, a novel non-purine selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase, therapy in allopurinol intolerant patients [abstract no. 803]. Arthritis Rheum 2004 Sep; 50 (9 Suppl.): S336
Schumacher HR, Becker MA, Wortmann RL, et al. The FOCUS trial 48-month interim analysis: long-term clinical outcomes of treatment with febuxostat in subjects with gout in an ongoing phase 2, open-label extension study [abstract no. OP0130]. Ann Rheum Dis 2006 Jul; 65 Suppl. II: 93
Data on file. TAP Pharmaceutical Products, 2006 Mar 9
Prometheus Laboratories Inc. Zyloprim® (allopurinol): product information [online]. Available from URL: http://www.prometheuslabs.com/pi/Zyloprim.pdf [Accessed 2005 Dec 8]
Acknowledgements and Disclosures
The manuscript was reviewed by: L.X. Chen, University of Pennsylvania and the VA Medical Center, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA; N.L. Edwards, Department of Medicine, University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida, USA; N. Schlesinger, UMDNJ-Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, New Jersey, USA; H.R. Schumacher Jr, University of Pennsylvania and the VA Medical Center, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA.
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding. During the peer review process, the manufacturer of the agent under review was offered an opportunity to comment on this article. Changes resulting from comments received were made on the basis of scientific and editorial merit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hair, P.I., McCormack, P.L. & Keating, G.M. Febuxostat. Drugs 68, 1865–1874 (2008). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-200868130-00006
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-200868130-00006